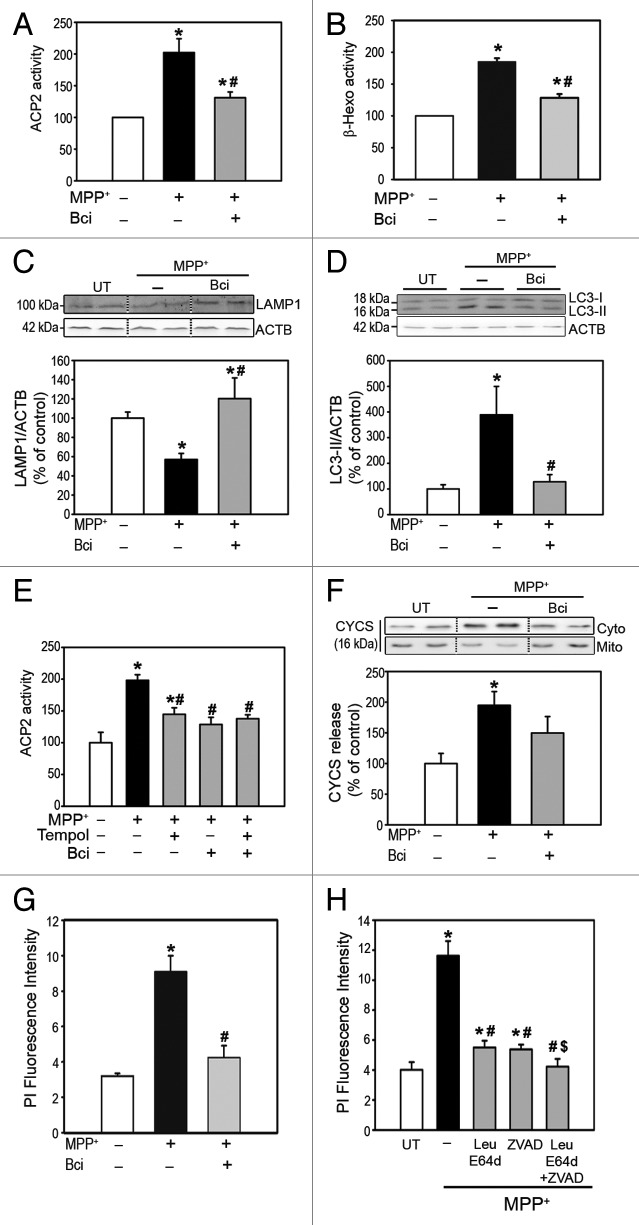
Figure 4. Pharmacological inhibition of BAX channel activity in MPP+-treated cells. (A andB) Enzymatic activities of (A) ACP2 and (B) β-hexosaminidase in lysosomal-free cytosolic fractions from MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells, in the presence or the absence of Bci. (C) LAMP1 immunoblot levels in total protein homogenates from MPP+-treated cells, in the presence or the absence of Bci. (D) LC3-II immunoblot levels in total protein homogenates from MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells, in the presence or the absence of Bci. (E) ACP2 activity in lysosomal-free cytosolic fractions from MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells, in the presence or the absence of Bci and/or Tempol. (F) Immunoblot levels of CYCS in cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions from MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells, in the presence or the absence of Bci. (G) Quantification of cell death by flow cytometry following propidium iodide staining in MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells, in the presence or the absence of Bci. (H) Cell death quantified by flow cytometry after propidium iodide staining in MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells in the presence or the absence of leupeptin/E64d and/or pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk. In all panels, data represent mean ± SEM from at least 3 independent experiments. Treatments were performed for 24 h (MPP+, 250 μM; Bci, 2 μM; Tempol, 500 μM; leupeptin, 100 μM; E64d, 10 μg/μl; z-VAD-fmk, 50 μM). *P < 0.05, compared with control cells, #P < 0.05 compared with MPP+-treated cells, $P < 0.05 compared with MPP+-intoxicated cells treated with either leupeptin/E64d or z-VAD-fmk.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.