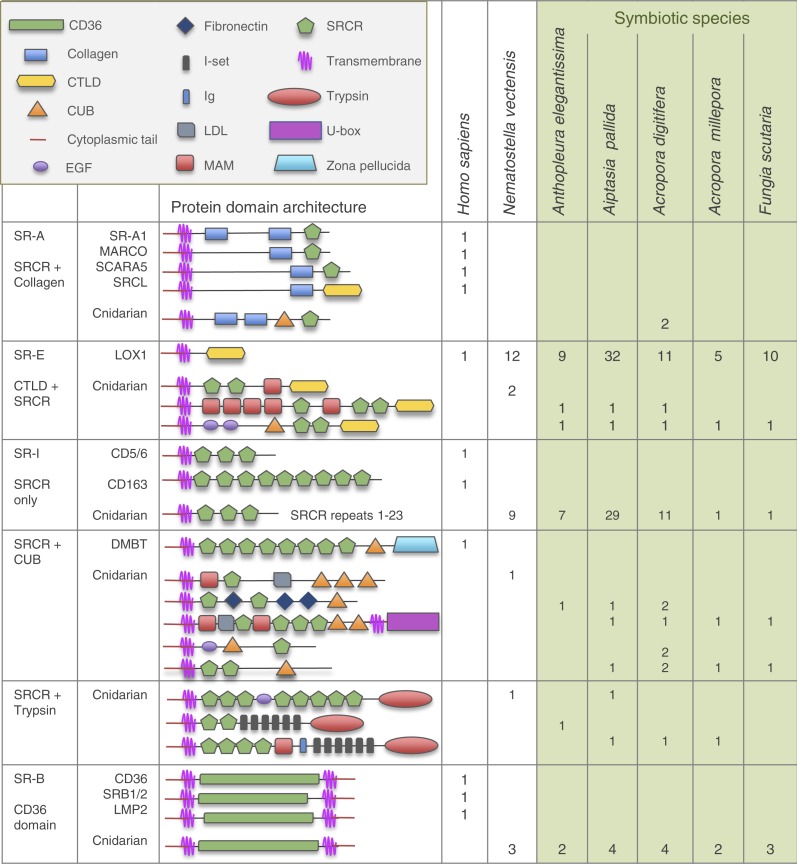
Figure 2. Domain architecture of cnidarian SR domains in the six resources searched compared to human SRs.
Identified cnidarian SR-A-like and SR-E-like sequences display diverse domain architecture and include novel domain combinations not found in vertebrates. SR-I-like sequences had a varying number of SRCR repeats. A variety of SRCR-domain-containing cnidarian sequences identified did not fit the criteria of any vertebrate SR classes and are presented as SRCR + CUB domains or SRCR + trypsin domains. SR-B-like domain combinations closely resembled vertebrate SR-Bs with two transmembrane domains, two cytoplasmic tails and a CD36 domain. CTLD, C type lectin domain; CUB, complement C1r/C1s, Uegf, BMP1; DMBT, deleted in malignant brain tumor protein; Ig, immunoglobulin; I-Set, intermediate set of immunoglobulin domain; LDL, low density lipoprotein; LOX1, lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor 1; EGF, epidermal growth factor; MAM meprin/A5-protein/PTPmu; MARCO, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure; SCARA5, scavenger receptor class A member 5; SRCL, scavenger receptor with C-type lectin; SRCR, scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain; U-box, ubiquitin box. Human SR data taken from Canton, Neculai & Grinstein (2013) (See File S1 for sequence information.).