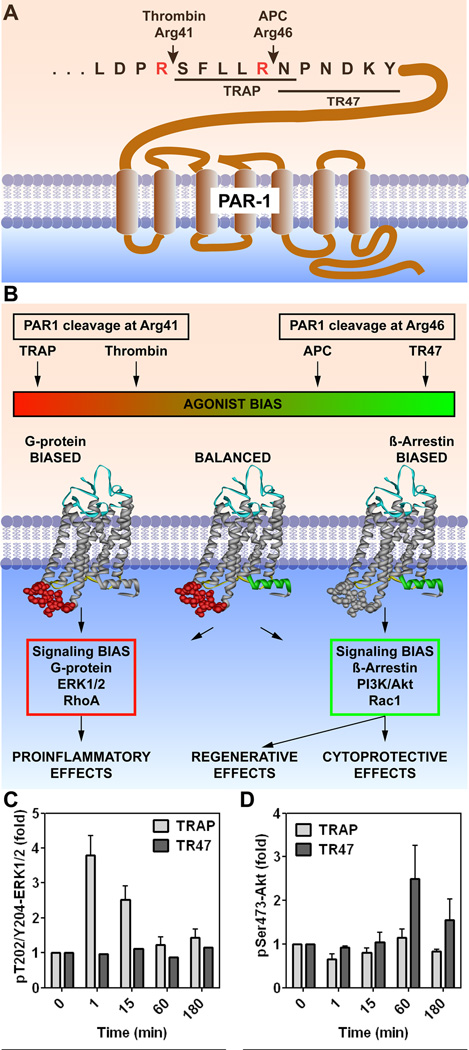
Figure 3. PAR1-dependent biased signaling initiated by thrombin or APC.
(A) PAR1 cleavage at Arg41 by thrombin results in the N-terminal tethered peptide agonist which begins with residue Ser42 (SFLLRN-etc.) whereas cleavage at Arg46 by APC results in a different N-terminal tethered agonist which begins with residue Asn47 (NPNDKY-etc.). (B) Thrombin’s cleavage results in G protein-dependent signaling (red box) whereas APC’s cleavage results in β-arrestin 2-dependent signaling (green box). (C) and (D) Synthetic peptides designated TRAP (Thrombin Receptor Activating Peptide) that begin with amino acid Ser42 cause thrombin-like effects on cells whereas a 20-mer synthetic peptide that begins with amino acid Asn47 (TR47) causes APC-like effects on cells.58,63–65 These consequences are illustrated by the differences in phosphorylations of ERK1/2 (C) compared to Akt (D); notably, TRAP induces phosphorylation of ERK1/2 but not Akt whereas TR47 induces phosphorylation of Akt but not ERK1/2.64 This figure is modified from Griffin et al, Blood, 2015.17