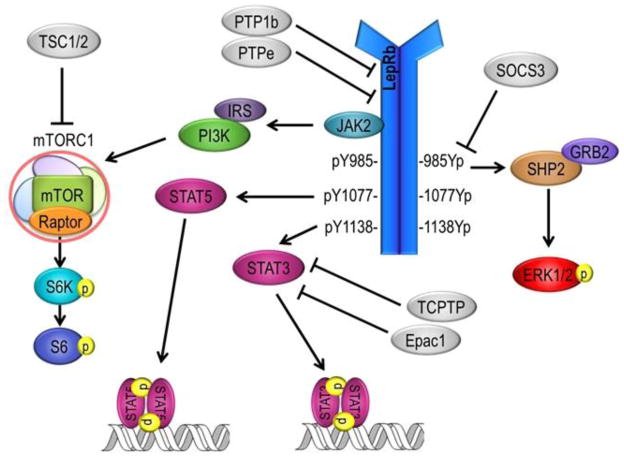
Figure 1.
Activation of the long signaling form of the leptin receptor (LepRb) initiates multiple distinct intracellular signaling cascades, which are thought to differentially contribute to the metabolic and cardiovascular sympathetic effects of leptin. Abbreviations: Epac1, exchange factor directly activated by cAMP 1; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2; GRB2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; JAK2, janus kinase 2; LepRb, leptin receptor b; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; mTORC1, mTOR complex 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PTP1b, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1b; PTPe, protein tyrosine phosphatase e; Raptor, regulator-associated protein of mTOR; S6, ribosomal protein S6; S6K, S6 kinase; SHP2, Src-homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; Stat3 and 5, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and 5; TCPTP, T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase; TSC1/2, Tuberous sclerosis protein 1 and 2.