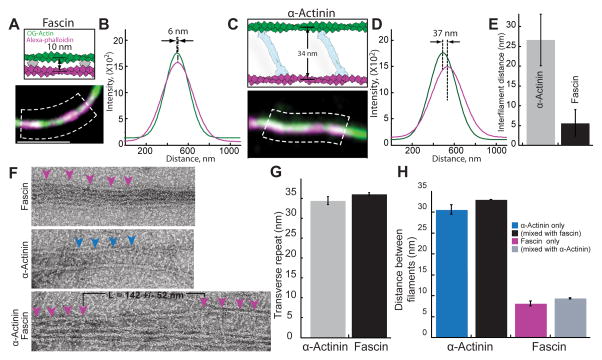
Figure 4. Actin filaments are spaced differently in bundles formed by fascin and α-actinin.
(A–E) Three-color TIRFM of bundles formed with 100 nM TMR-fascin and 400 nM α-actinin between a preassembled filament stabilized with alexa-647-phalloidin (magenta) and 1.5 μM spontaneously assembled Mg-ATP actin (33% Oregon green-actin).
(A and C) Schematics of predicted outcomes (top) [8, 14], and merged micrographs of two-filament bundles (bottom), for (A) fascin and (C) α-actinin. Scale bar=2 μm.
(B and D) Plots of average fluorescence intensities across a normal line (white lines in dashed boxes (A) and (C)) for two-filament bundles formed by (B) fascin and (D) α-actinin. Distances between the centroids of the bundled filaments were revealed by curve fits to a Gaussian.
(E) Average distance between filaments within α-actinin or fascin domains. Error bars indicate SEM; n≥6 bundles.
(F–H) Electron microscopy of F-actin bundles negatively stained with uranyl acetate, which were formed from 1.5 uM actin.
(F) Micrographs of bundles with 1 μM fascin (top), 800 nM α-actinin (middle) or both (1 μM α-actinin 0.25 μM Fascin (bottom). Magenta and blue arrowheads indicate fascin and α-actinin molecules. L = the length of the transition zone. Scale bar=30 nm.
(G) Distance of transverse repeat in fascin and α-actinin bundles. Error bars indicate SEM; n≥10 bundles.
(H) Distance between filaments in a fascin and α-actinin bundles. Error bars indicate SEM; n≥8 bundles.