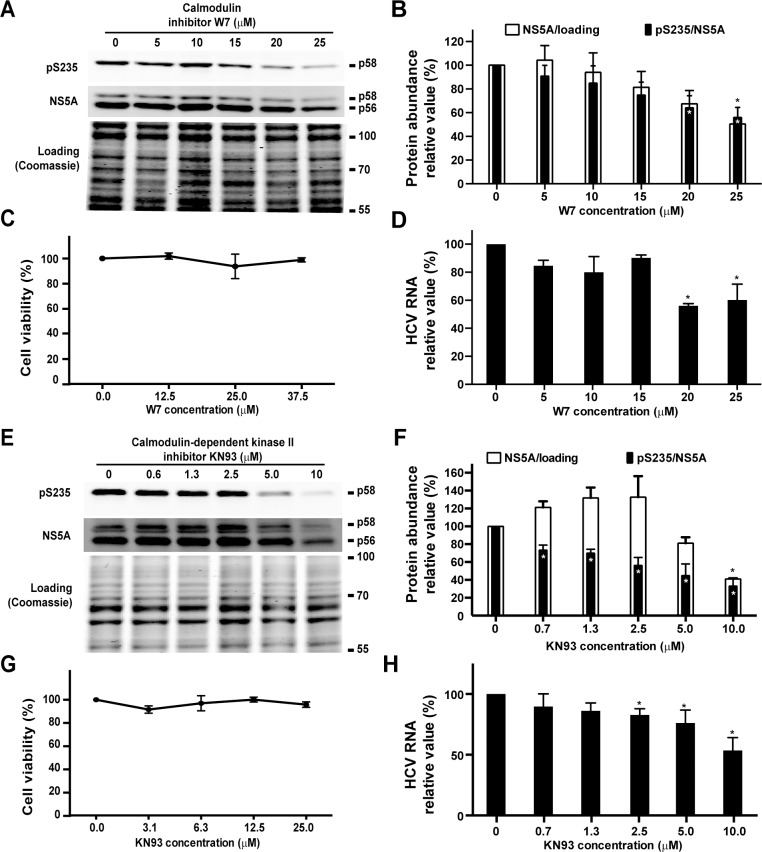
Fig 3. Calmodulin and CaMKII inhibitors reduced NS5A S235 phosphorylation and HCV RNA levels in the infected Huh7.5.1 cells.
(A and E) Representative and (B and F) summary of the immunoblotting for NS5A and NS5A phosphorylation at S235 (pS235) in the HCV (J6/JFH1)-infected Huh7.5.1 cells. The HCV-infected cells (3 days) were exposed to the inhibitors for 1 day before the immunoblotting analysis. Values are Mean ± SEM (n = 3). Asterisk indicates significance i.e. p<0.05, t-test against the values in the vehicle controls (0 μM). Protein abundance was quantified with the Li‐Cor scanner, adjusted for the loadings (i.e. Coomassie staining) and normalized with the values in the vehicle control cells (0 μM). (C and G) Cell viability assessed with the MTT assay. The cells were exposed to the inhibitors for 1 day before the MTT assay. (D and H) Quantitative measurements of the HCV RNA levels in the HCV-infected Huh7.5.1 cells exposed to the inhibitors. The experiments were done as those in a-c and e-g except that RNA was collected for the analysis. The GAPDH mRNA levels were analyzed in parallel for the loadings. Relative RNA abundance was normalized to the values of the vehicle controls (0 μM).