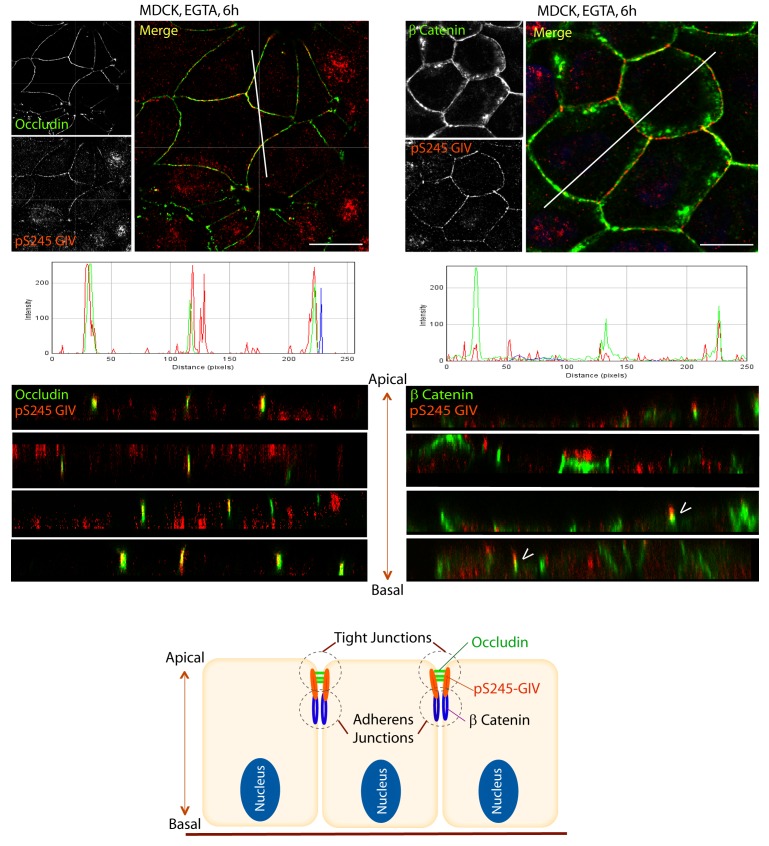
Figure 3. S245-phosphorylated GIV (pS245-GIV) localizes preferentially to tight junctions (TJs).
MDCK cells were grown to full confluency into domed monolayers prior to exposing them to the Ca2+ chelator EGTA for 6 hr prior to fixation. Fixed cells were co-stained for pS245-GIV (red) and either the TJ-marker Occludin (Left; green) or the AJ-marker β-Catenin (Right; green) and analyzed by confocal microscopy (z-stack projections and x-z cross-sections). Top: Representative confocal images are shown, each taken at the level of the TJs (marked by Occludin; left) and AJs (marked by β-Catenin; right). Middle: RGB profiles showed that pS245 GIV colocalized with Occludin but not β-Catenin. Bottom: Sections through the 3D reconstruction of a confocal Z-stack confirms that, in most instances the pS245-GIV colocalizes with the TJ marker Occludin, and lies just apical to the AJ marker β-Catenin. In some cases (arrowheads), the lower pole of the pS245-GIV signal partially colocalizes with the upper pole of the β-Catenin signal. Schematic summarizes the localization of pS245-GIV and its relationship to the TJ and AJs. Scale bar = 25 μm.