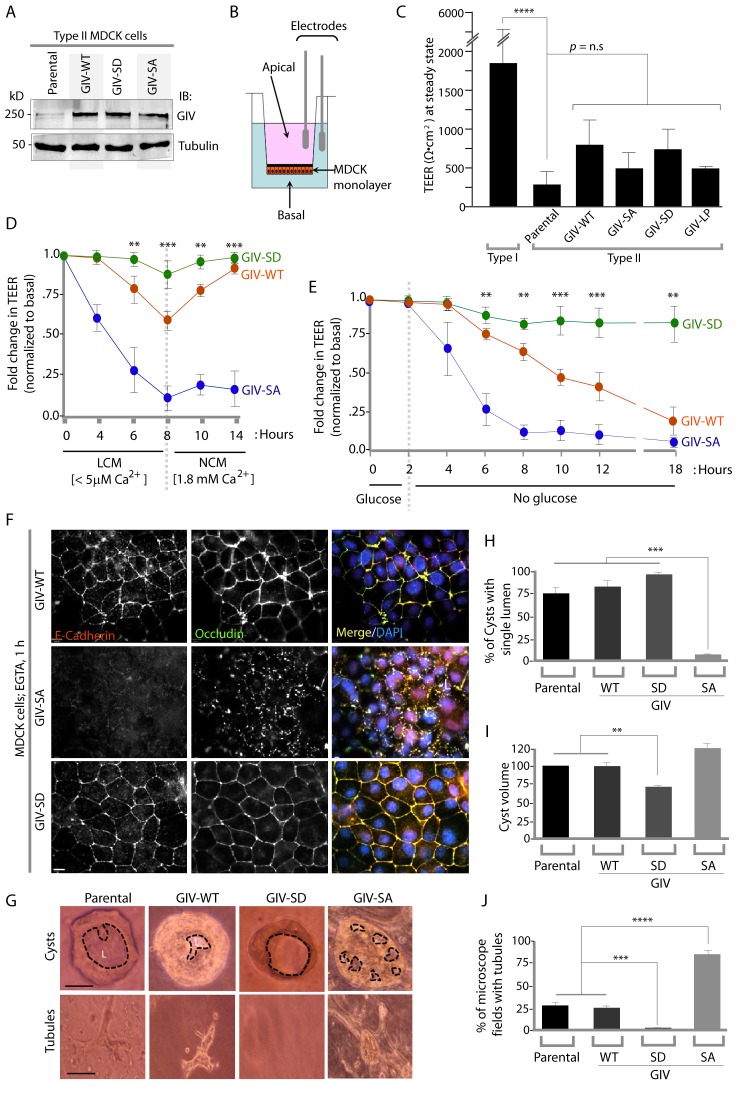
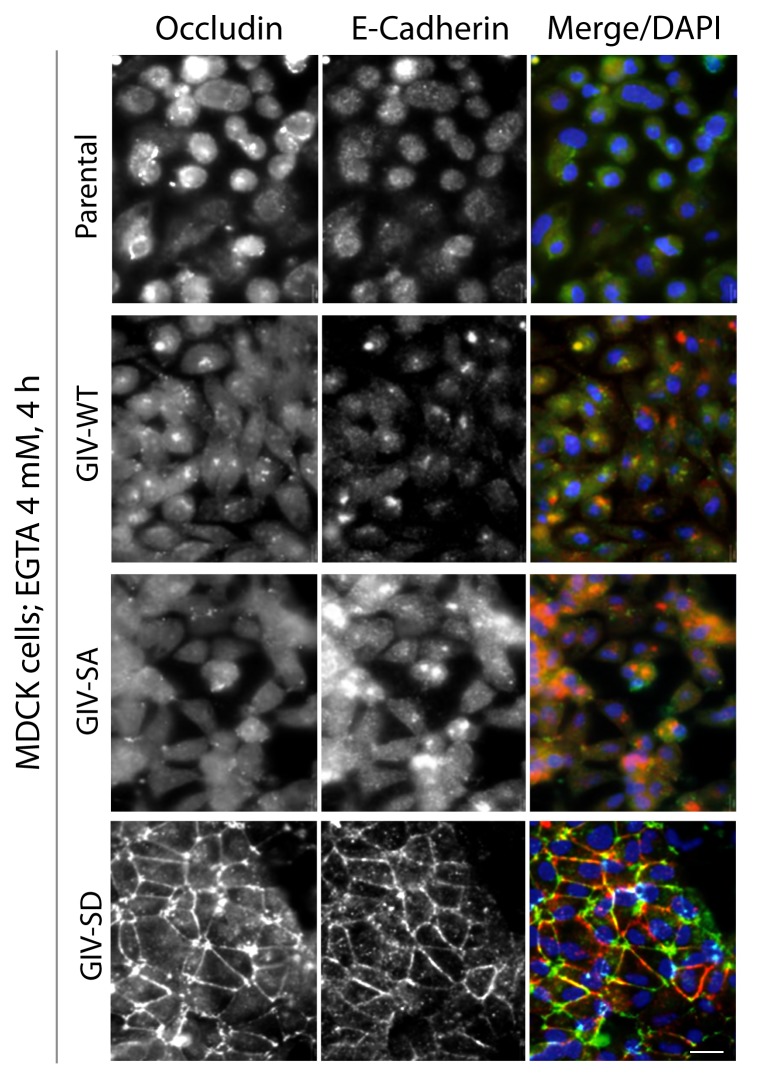
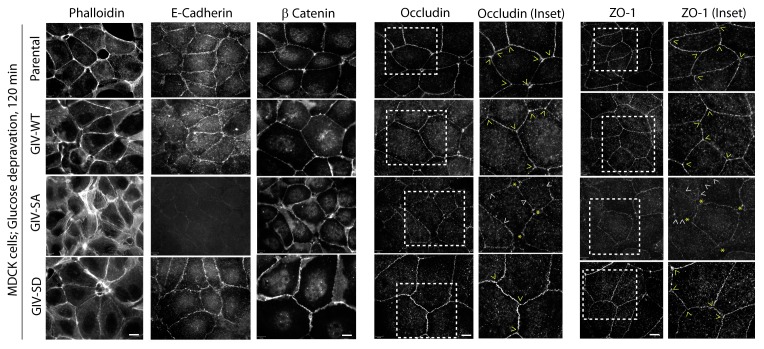
Figure 4. Phosphorylation of GIV at S245 stabilizes tight junctions (TJs) under low-calcium states and is essential for epithelial barrier function and morphogenesis.
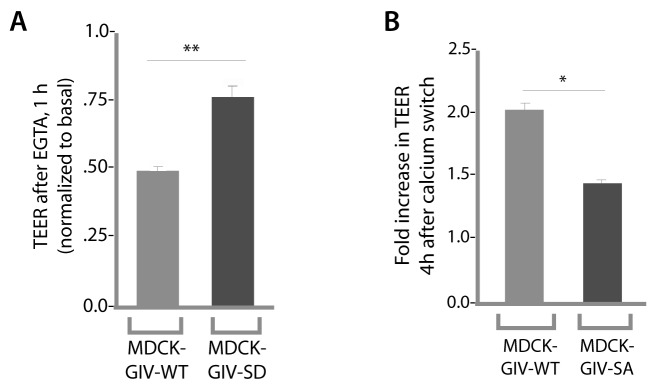
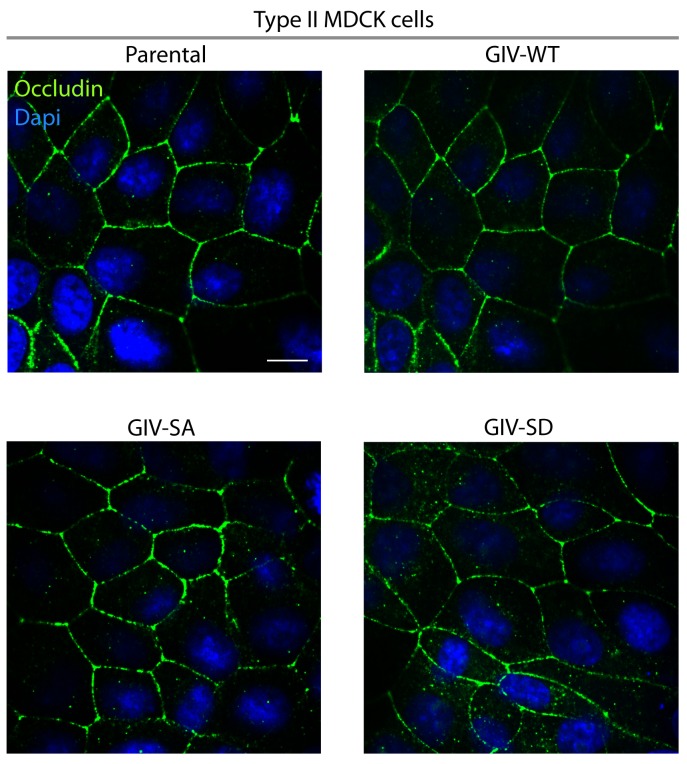
(A) Whole cell lysates of MDCK cells stably expressing wild-type GIV (GIV-WT), or non-phosphorylatable (S→A; GIV-SA), or phospho-mimicking (S→D; GIV-SD) mutants of GIV were analyzed for GIV and tubulin by immunoblotting. (B–C) Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was measured using a Millicel-ERS resistance meter across fully polarized domed monolayers of various MDCK cell lines grown to domed confluency in Transwell inserts (schematic shown in B) in the presence of full growth media with normal calcium. Bar graphs (C) display the TEER measured across each cell line. As expected, type I MDCKs exhibit higher TEER than type II cells. No significant differences were noted between the MDCK-GIV cell lines stably expressing the various GIV constructs. n = 3. Results are expressed as ± SEM. ****p<0.0001. (D–E) Changes in TEER was measured across monolayers of various MDCK cell lines during exposure to low-calcium media (LCM; left), followed by switching to normal calcium media (NCM; right) or during energetic stress when exposed to media without glucose. Graphs in D and E show that compared to MDCK-GIV-WT cells, TEER rapidly dropped across MDCK-GIV-SA monolayers exposed to LCM (D) as well as energetic stress (E) but relatively preserved in MDCK-GIV-SD cells. This drop is rapidly and completely reversed upon exposure to NCM in MDCK-GIV-WT and SD cells, but remains impaired in MDCK-GIV-SA cells. n = 3. Results are expressed as ± SEM. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; **p<0.01. (F) MDCK-GIV cell lines were grown to full confluency into domed monolayers, treated with EGTA for 1 hr, and subsequently fixed. Fixed cells were stained for E-cadherin, Occludin, and DAPI (nuclei; blue), and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Images displayed are representative of 13–15 HPF images captured at 60X mag in each cell line. Preservation of TJs and AJs, as visualized using Occludin and E-Cadherin as markers, was significantly higher in MDCK-GIV-WT and MDCK-GIV-SD [65–90% of the imaged surface area; n = 15 randomly imaged fields in each cell line], but not in MDCK-GIV-SA cell lines [0–4% of the imaged surface area; n = 13 randomly imaged fields; p<0.001]. Scale bar = 10 μm. See also Figure 4—figure supplements 2 and 3 for the findings at baseline and at 4 hr time point. (G) Parental MDCK cells and various MDCK-GIV cell lines were seeded and grown in collagen-containing matrix for 2 weeks and analyzed for the formation of cyst and tubular structures by light microscopy. Representative cysts and tubular structures are shown for each cell line. L = lumen. Scale bar = 50 μm. (H–J) Bar graphs display the % of cysts with single lumens (Y axis; H), cyst volume (Y axis; I) and % fields with tubule formations (Y axis; J) seen in each cell line in G. Absolute numbers for cyst volume were normalized to parental cells (set to 100%). Three independent experiments comprising 450–600 cysts per cell line are summarized. Results are expressed as ± SEM. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.
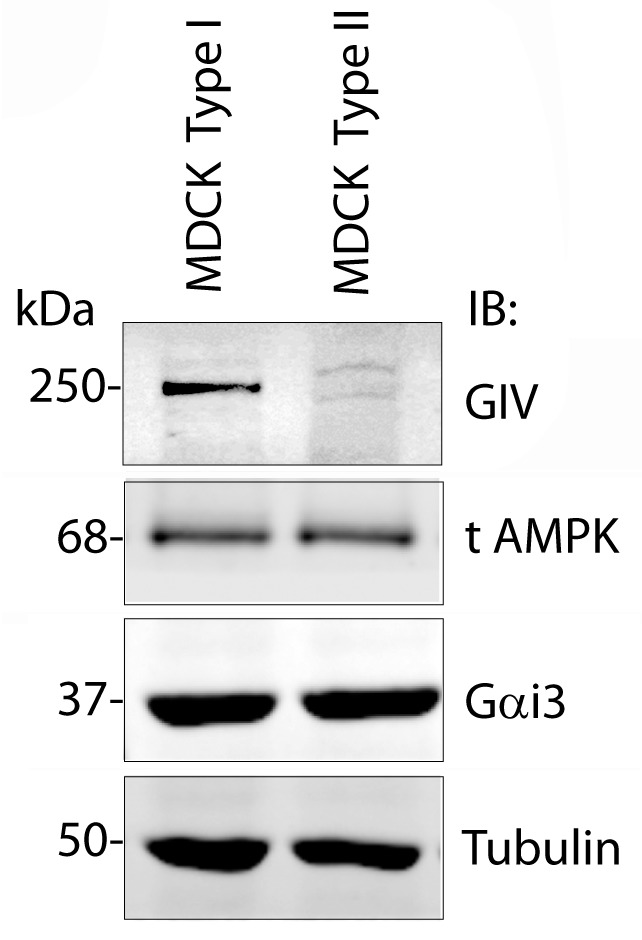
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. A comparison of levels of GIV expression in Type I vs Type II MDCK cells.