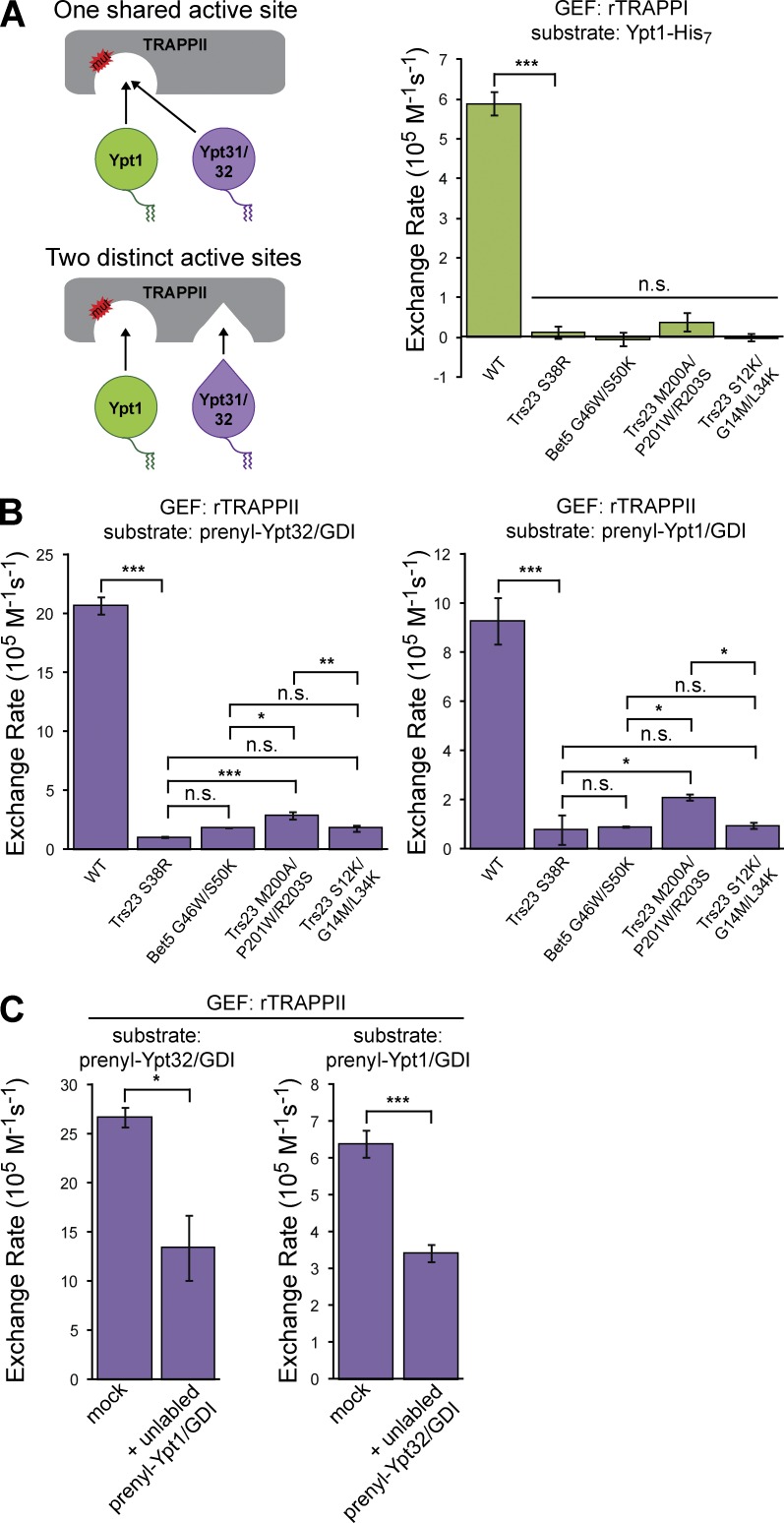
Figure 2.
Ypt31/32 and Ypt1 share an active site in TRAPPII. (A, left) Schematic depicting two possible mechanisms for TRAPPII-mediated Ypt31/32 activation. (right) The indicated rTRAPPI active site mutants were tested for their ability to activate Ypt1-His7 in the presence of TGN liposomes. Error bars represent 95% CIs for n ≥ 3 reactions. (B) rTRAPPII active site mutants were tested for their ability to activate prenylated-Ypt32/GDI and prenylated-Ypt1/GDI in the presence of TGN liposomes. Error bars represent 95% CIs for n ≥ 2 reactions. (C) rTRAPPII-mediated activation of mantGDP-labeled prenylated-Rab/GDI substrates on TGN liposomes in the absence (mock) or presence of equimolar concentrations of competing unlabeled prenylated-Rab/GDI complexes. Error bars represent 95% CIs for n ≥ 3 reactions. n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.