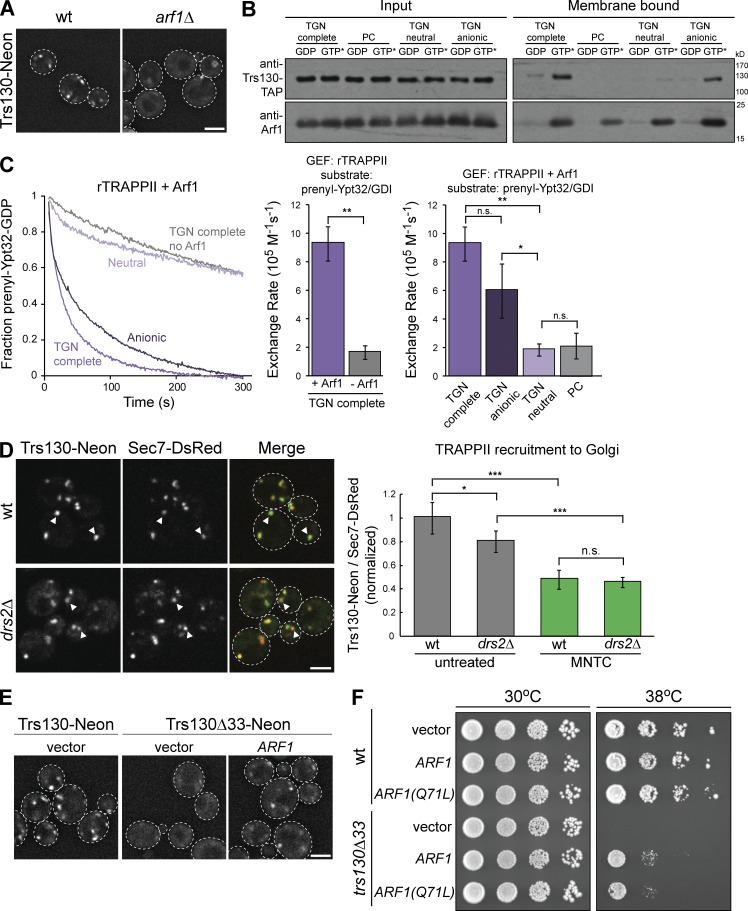
Figure 5.
Activated Arf1 and anionic lipids cooperate to recruit TRAPPII to membranes in vitro and in vivo. (A) Localization of Trs130-mNeonGreen in WT versus arf1Δ yeast grown at 30°C. (B) Liposome flotation assay testing TRAPPII recruitment to different membranes by activated myristoylated-Arf1. Proteins were visualized by Western blot. Liposomes do not contain Ni2+-DOGS (see Materials and methods). GTP* indicates GMP-PNP. (C, left) Representative normalized traces showing rTRAPPII-catalyzed prenylated-Ypt32/GDI activation in the presence or absence of activated myristoylated-Arf1 on synthetic TGN liposomes, liposomes containing only anionic or neutral TGN lipids, or PC liposomes. Liposomes do not contain Ni2+-DOGS. (right) Rates of Ypt32 activation determined from the traces at left. Error bars represent 95% CIs for n ≥ 3 reactions. (D, left) Localization of Trs130-mNeonGreen relative to the late Golgi marker Sec7-6xDsRed in WT versus drs2Δ yeast grown at 30°C. (right) Recruitment of TRAPPII to Golgi compartments was measured by quantifying the ratio of Trs130-mNeonGreen to Sec7-6xDsRed in Sec7-6xDsRed puncta. Recruitment was measured in untreated cells and cells treated with MNTC for 10 min. Error bars represent 95% CIs for n ≥ 62 compartments. (E) Arf1 expressed on a low-copy plasmid partially rescues localization of trs130Δ33 mutant TRAPP complexes in yeast grown at 30°C. (F) Constitutively active or WT Arf1 was expressed on low-copy plasmids to test the ability of Arf1 to rescue growth in temperature-sensitive trs130Δ33 mutant cells. Arf1(Q71L) is a GTP-locked mutant. Bars, 2 µm. White arrowheads denote colocalization of Trs130-mNeonGreen and Sec7-DsRed at Golgi compartments. n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.