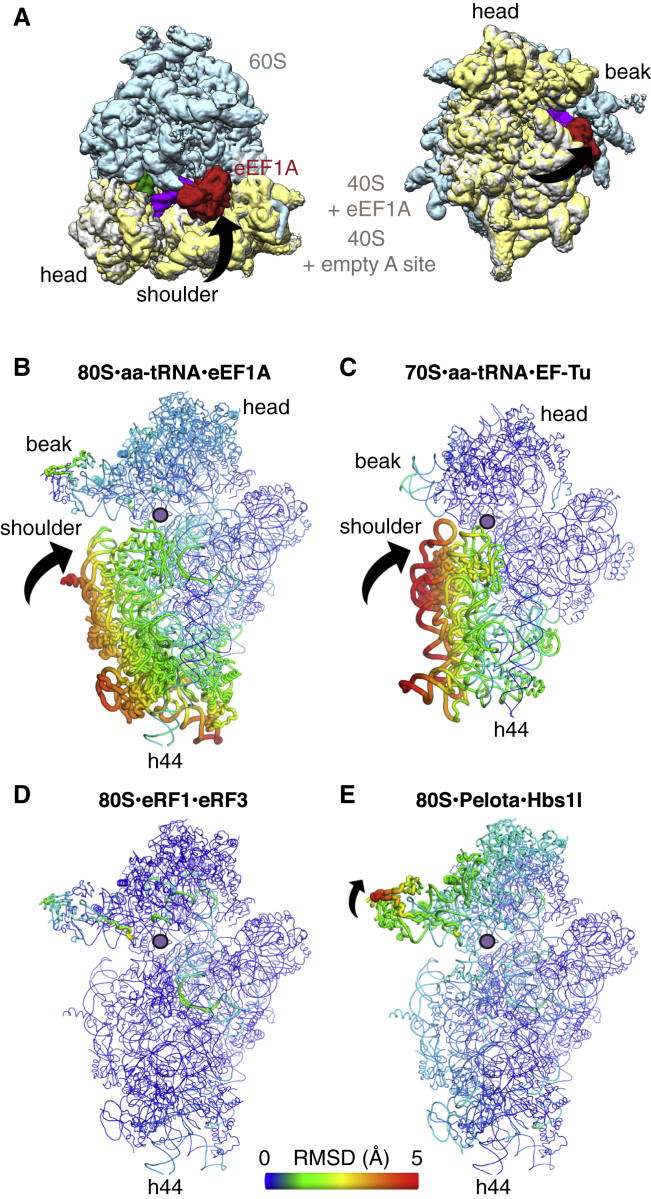
Figure 4.
Conformational Responses of the Ribosome to Decoding Complexes
(A) EM map of the elongation complex (colored) superposed on a ribosome with an empty A site (gray small subunit), demonstrating the movement corresponding to domain closure (illustrated by the arrow). The shoulder region of the small subunit moves toward the large subunit, which maximizes the contacts between a translational GTPase and the ribosome, particularly with the GTPase center.
(B–E) Worm diagrams colored by pairwise root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) of the small subunits of (B) the elongation complex relative to a ribosome with an empty A site, (C) of a bacterial elongation complex (PDB: 5AFI) relative to an empty ribosome (PDB: 4UY8), and of the (D) termination and (E) rescue complexes relative to the same reference as in (B). The directions of movements are indicated by arrows. The A site is indicated with a purple dot.