Figure 7.
Conformational Changes during Accommodation
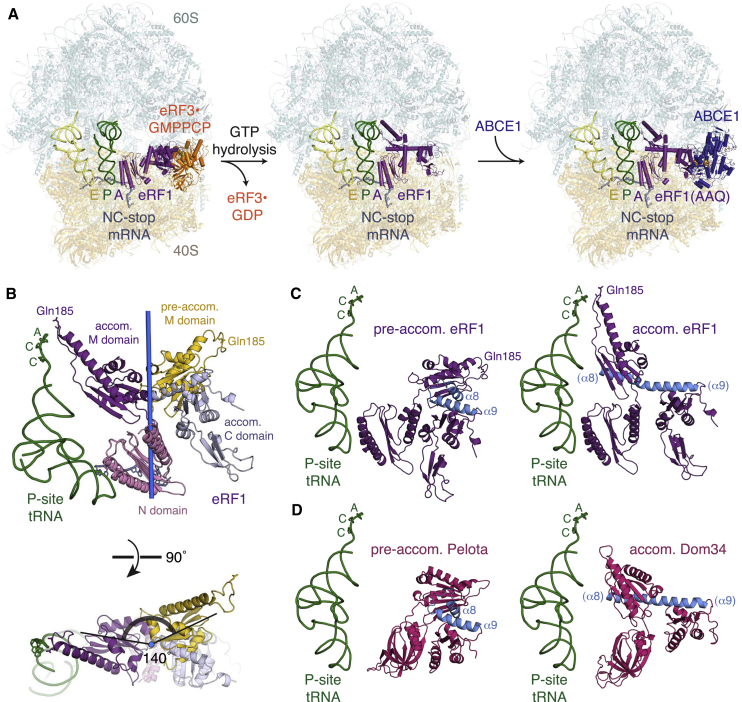
(A) Structures of ribosomal complexes representing intermediates along the eukaryotic translation termination pathway.
(B) The accommodated M domain (purple) of eRF1 is rotated by 140° relative to the pre-accommodated state (yellow). Gln185 of the catalytic GGQ motif, P-site tRNA (green), the N domains in both states (pink), the C domain (pale blue) in the accommodated state, and the axis of M domain rotation (blue) are shown.
(C) Comparison of eRF1 (purple) in a pre-accommodated state (left) with an accommodated (right) conformation, showing straightening of α8 and α9 (blue) into a continuous helix upon accommodation.
(D) Comparison of Pelota (pink) in a pre-accommodated state (left) with Dom34 (pink) in an accommodated (right) state (right; PDB: 3IZQ), revealing straightening of α8 and α9 (blue).
See also Figure S7.