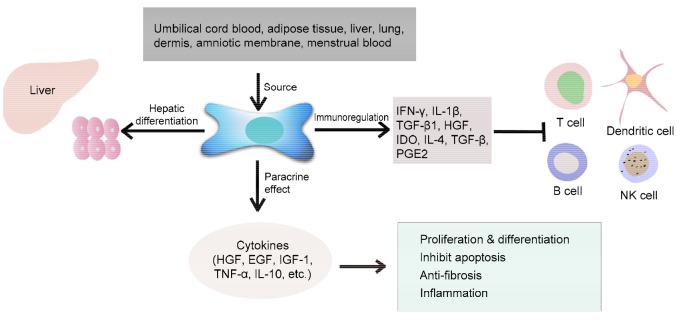
Fig. 1.
Sources and function of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
The sources of MSCs are abundant, including umbilical cord blood, adipose tissue, liver, lung, dermis, amniotic membrane, and menstrual blood, among others. MSCs can differentiate into hepatocytes, secrete various cell factors, and participate in immunoregulation. IFN-γ: interferon gamma; IL: interleukin; TGF: transforming growth factor; HGF: hepatocyte growth factor; IDO: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; EGF: epidermal growth factor; IGF: insulin-like growth factor; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; NK cells: natural killer cells