Figure 1.
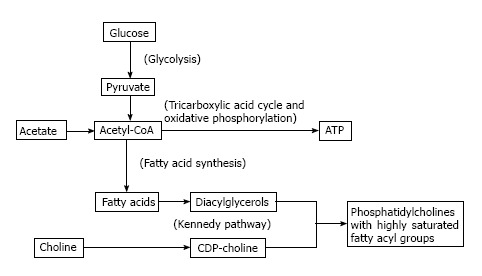
The interplay between glucose, acetate, and choline metabolism. By providing substrate for de-novo fatty acid synthesis, acetate metabolism may feed into phosphatidylcholine synthesis, explaining why tumors showing high uptake of 11C-acetate may also show increased uptake of radiolabeled choline on PET. Because acetyl-CoA produced from acetate may also serve as a substrate for the citric acid cycle and other pathways, it is possible that, for some cancers, 11C-acetate uptake may not always provide a consistent readout of tumor lipogenesis. The Kennedy pathway is an ATP-dependent pathway that may rely to varying degrees on glycolysis as a source of ATP. ATP: Adenosine triphosphate.
