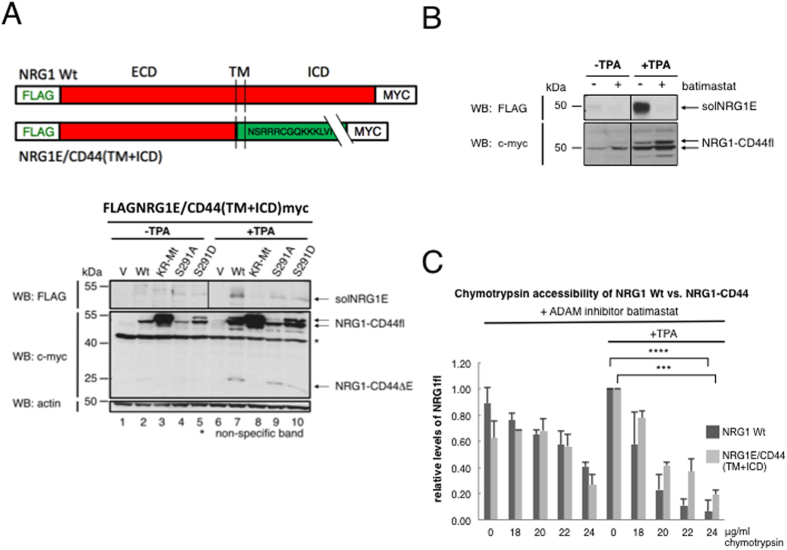
Figure 6.
(A–C) ICDs modulate cleavage and protease accessibility of “foreign“ ectodomains in chimeras of CD44 and NRG1. (A) NRG1E/CD44(TM + ICD): CD44 ICD regulates cleavage of NRG1 ectodomain; effect of CD44 ICD mutants. See sketch for construction of chimeras. (B) Induced cleavage of NRG1E/CD44(TM + ICD) is inhibited by batimastat. (C) NRG1 wt and NRG1E/CD44(TM + ICD) show similar protease accessibility. (A,B) NRG wt and the NRG1E/CD44(TM + ICD) chimera were expressed in HEK293T cells E = ectodomain, TM = transmembrane domain, ICD = intracellular domain. The chimeric construct and its CD44 ICD mutants were transfected into RPM-MC cells and cleavage by TPA was analyzed as in Fig. 2. V = vector control. Wt = wild type. Batimastat (10 μM) was added 15 min prior to TPA. In (A) upper panel the solNRG1E samples were run on one gel, however an empty lane without sample that separated −TPA and +TPA was removed. The samples of the middle and lower panels were run on the same gel. The samples of (B) were also run on one and the same gel but several lanes that showed other samples were removed. (C) Protease accessibility regulation by TPA in the presence of batimastat (10 μM) was determined as in Fig. 1B. Column diagrams show mean values of relative level of ectodomain cleavage ± SD from three independent experiments.