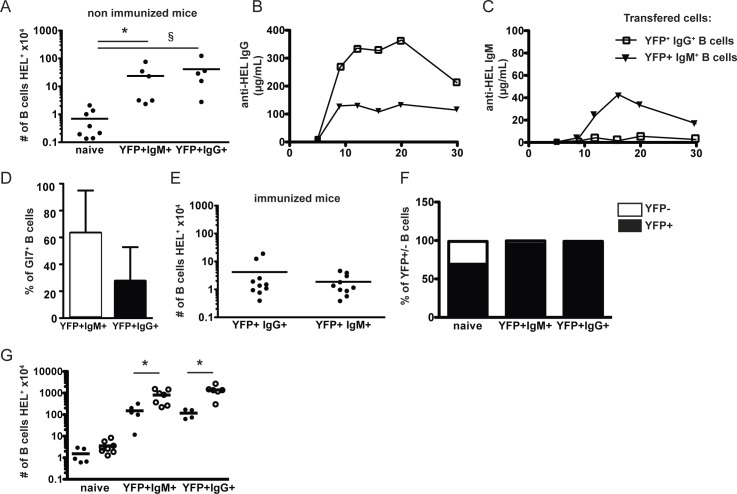
Fig 5. Functions of AID/YFP+ memory B cell subsets.
Rag2-/- recipient mice were injected with naive SWHEL.AID/YFP.Rag2-/- B cells and OTII.Rag2-/- naive CD4 T cells and immunized as in Fig 1. Eight weeks after immunization, AID/YFP+ IgM+ and AID/YFP+ IgG+ subsets were isolated and transferred alone into secondary Rag2-/- recipient mice. Naive B cells were transferred as controls. (A) Numbers of splenic B cells recovered from the different secondary hosts without immunization. (B) The secondary hosts were immunized 1 day after transfer and the seric levels of anti-HEL specific IgG (C) and IgM were measured 6, 9, 12, 16, 20 and 30 days after immunization. (D) the % of splenic Gl7 hi B cells in secondary hosts transferred with YFP+ IgM+ (white) or YFP+ IgG+ (black) B cells was analyzed by Flow Cytometry 3 weeks after immunization and (F) the relative % of AID/YFP- and AID/YFP+ cells was assessed. In another settings, (G) the different secondary hosts were immunized either 1 day (black circles) or 30 days (white circles) after transfer and the number of total splenic B cells recovered from the spleen of different secondary hosts was determined 6 weeks after immunization. Data (mean ± SEM) are shown for one experiment representative of 2, with 4–5 mice per group. Significances were calculated using Student t-tests, *, P<0.05; ***, P<0.001.