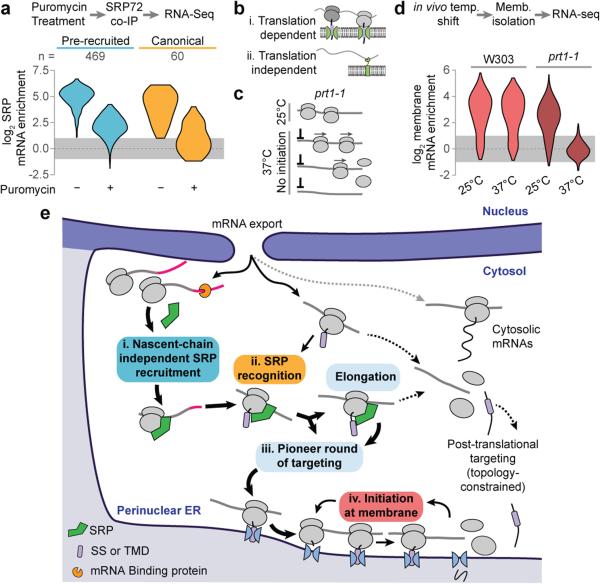
Figure 4. Translation and the role of SRP.
a, Distributions of RNA-seq SRP enrichment scores from secretory protein transcripts (SS, TMD, SS-TMD, or TA), with or without puromycin treatment. Included ORFs have at least 2-fold SRP enrichment without puromycin. b, The prt1-1 allele prevents initiation at non-permissive temperatures. Translational run-off removes all ribosomes from transcripts. b, Transcripts are retained on the membrane though binding of the RNC to the translocon. It is also possible that mRNA binding proteins at the ER bind transcripts. c, Distributions of RNA-seq membrane enrichment scores of secretory protein transcripts (n = 584). d, After mRNA export, a pioneer round of targeting directs secretory transcripts to the ER membrane. SRP is specifically pre-recruited transcripts that will present a functional targeting signal. Upon emergence of an SS or TMD, SRP directs RNCs to the ER membrane. Once at the ER membrane, transcripts are retained over multiple rounds of translation.