Figure 1.
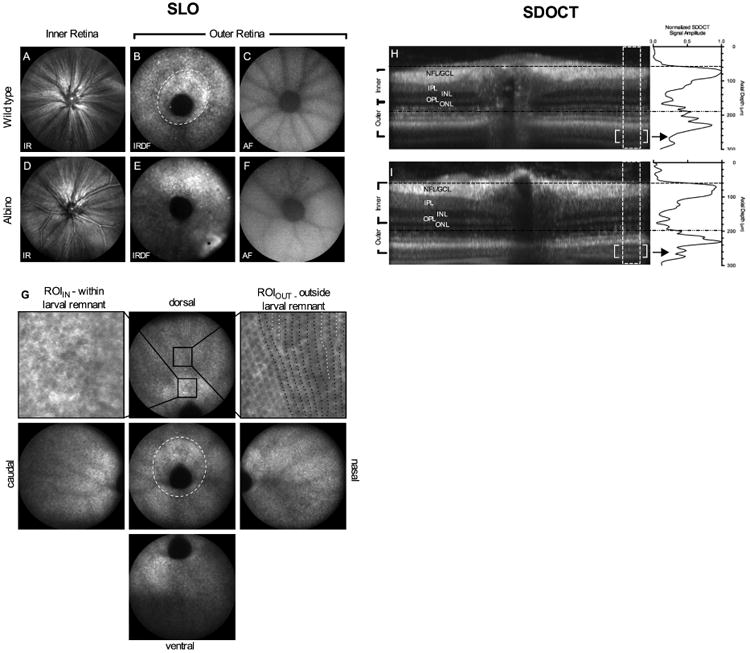
SLO and SDOCT images of retina from pigmented and albino zebrafish. IR reflectance images from the VRI (A, D). IRDF images from outer retina showing the optic disk and photoreceptor mosaic (B, E). Central and peripheral IRDF-SLO views acquired from a wild type fish (G) showing that photoreceptor organization is more easily discerned with increasing distance from the optic disk. Black arrows in the central view outline the larval remnant where photoreceptor morphology transitions from a disorganized to organized architecture between 20 and 36 dpf. Regions of interest from within (upper left) and outside (upper right) of the larval remnant are shown to reveal the hyporeflective nature of short single UV cones, the most proximal (i.e. vitreal aspect) of the three cone types found within this region. Within the larval remnant photoreceptors appear randomly distributed (upper left; arrows). In contrast, an ROI from outside the larval remnant shows hyporeflective short single cones appearing as spots oriented in vertical rows (upper right; black dotted lines). In this ROI, intercalation of new photoreceptor rows that occur as a result of animal growth can be visualized (upper right; white dotted lines) Native autofluorescence (488nm excitation/500-680 emission) images from the outer retina (C, F). SDOCT images show the similarities and/or differences between the in-depth morphology of pigmented (H) and albino (I) animals. Horizontal lines indicate the approximate locations where the VRI (H; black hashed lines) and outer retina (I; black hashed-dot-dot lines) that have been previously shown in SLO images (A, D and B, E), respectively. The lack of melanin pigment within melanosomes (M) of RPE apical processes in albino animals improves light penetration and imaging depth over pigmented animals (Fig. 1D vs. 1H; enclosed brackets). Within this region, additional structural detail can be discerned within the outer retina such as rod outer segments (ROS) and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Image dimensions: (A-F) ∼1mm, (G) standard views ∼ 1 mm and ROIIN & ROIOUT ∼ 0.13mm), & (H-I) - 0.3 mm (depth) × ∼1 mm (width).
