Figure 6. A model for direct force impact on gene activation.
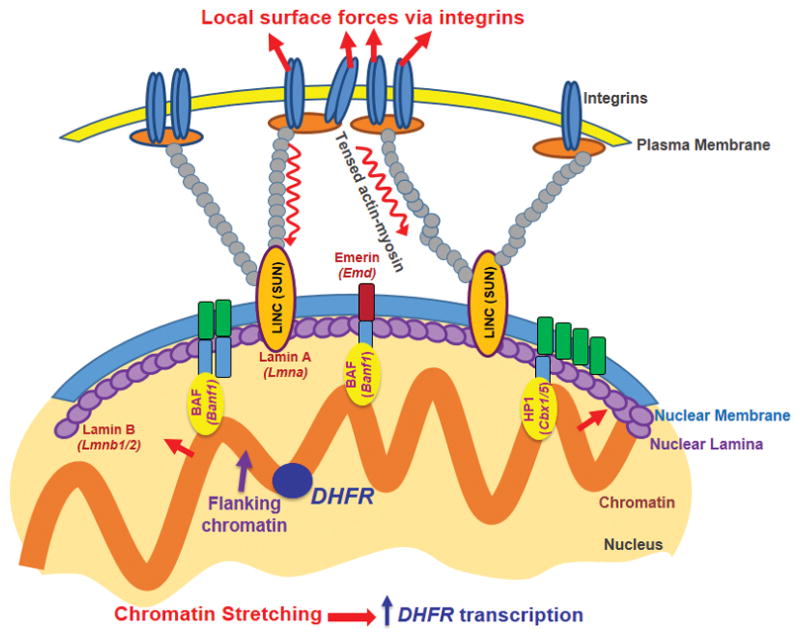
A local surface force via integrins is propagated though the myosin-II tensed actin cytoskeleton to the LINC (via SUN1 and SUN2) complex, to nuclear lamins, and then is transferred to the flanking chromatin through BAF and HP1 proteins and other molecules. The flanking chromatin transfers the force to deform and to stretch the chromatin segment containing the DHFR gene at the nuclear interior, facilitating binding of the RNA Polymerase II and transcription factors to upregulate DHFR transcription. Note that underneath each nuclear protein is its gene name. Not drawn to scale.
