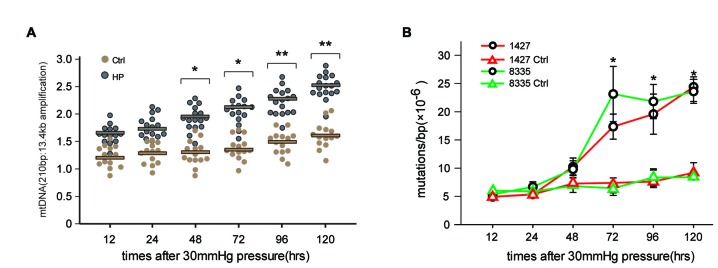
Figure 1.
Elevated hydrostatic pressure (HP; 30 mm Hg) led to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage and mutations in primarily cultured cells. (A) mtDNA damage in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) was determined by long-extension (LX)-PCR, based on the ratio of short to long amplicons at different times after the onset of exposure to increased HP (n = 4–7/time point/group). (B) After exposure to increased HP, the random mutation capture assay determined that the point mutation frequency in mtDNA increased at two independent sites. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Values are the means ± SEMs. HP, increased hydrostatic pressure; ctrl, control with normal pressure.