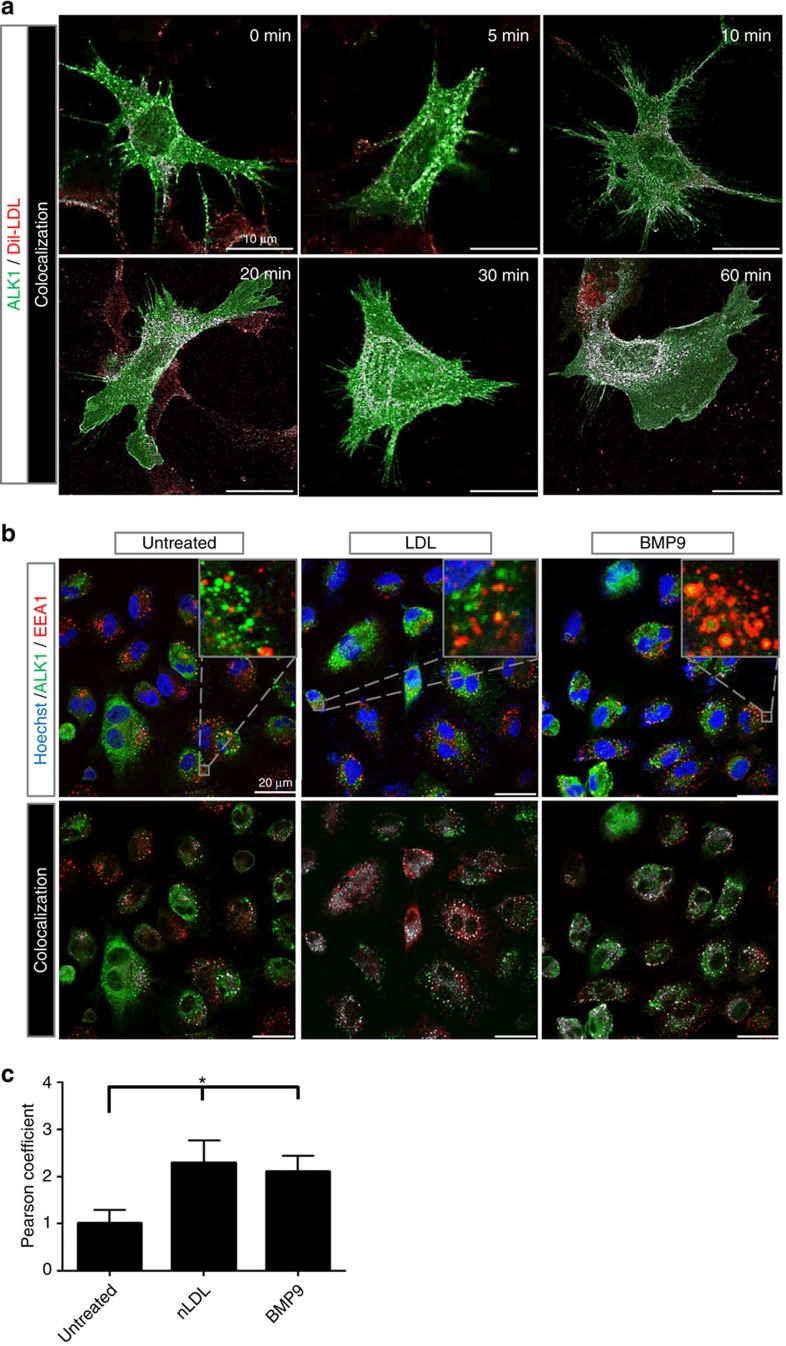
Figure 6. Time-dependent internalization and co-localization of DiI-LDL and ALK1.
(a) Ldlr-KO MEFs were infected with ALK1-GFP, incubated in LPDS overnight and the time-dependent internalization of DiI-LDL examined at 37 °C. Cells were imaged for ALK1-GFP (green), DiI-LDL (red) and white reflecting co-localization of ALK1-GFP/DiI-LDL (Menders correlation). The internalization of DiI-LDL and its co-localization with DiI-LDL shows at 10–20 min and accumulates in a perinuclear compartment after 60 min. Scale bar, 10 μm. The data is representative for three independent experiments. (b) Analysis of ALK1-GFP localization in control (untreated), LDL (25 μg ml−1) or BMP9 (10 ng ml−1) treated EA.hy926 cells. Cells were infected for 48 h and transferred to LPDS for the remaining 24 h. Cells were treated as described for 1 h at 37 °C, fixed and imaged. Upper panels show original confocal laser scanning microscopy images (green, ALK1-GFP; red, EEA1; blue, nuclei). Lower panels show Menders correlation (green, ALK1-GFP alone; red, EEA1 alone; white, ALK1-GFP/EEA1 co-localized). Scale bar, 20 μm. The data is representative for three independent experiments. (c) Bar graph shows Pearson correlation of these three conditions. The result indicates a co-localization of ALK1 with the early endosome marker EEA1 upon stimulation with either LDL or BMP9 within 1 h. Data represent the mean±s.e.m. and are representative of three experiments. *P<0.05, Student's t-test.