Figure 3.
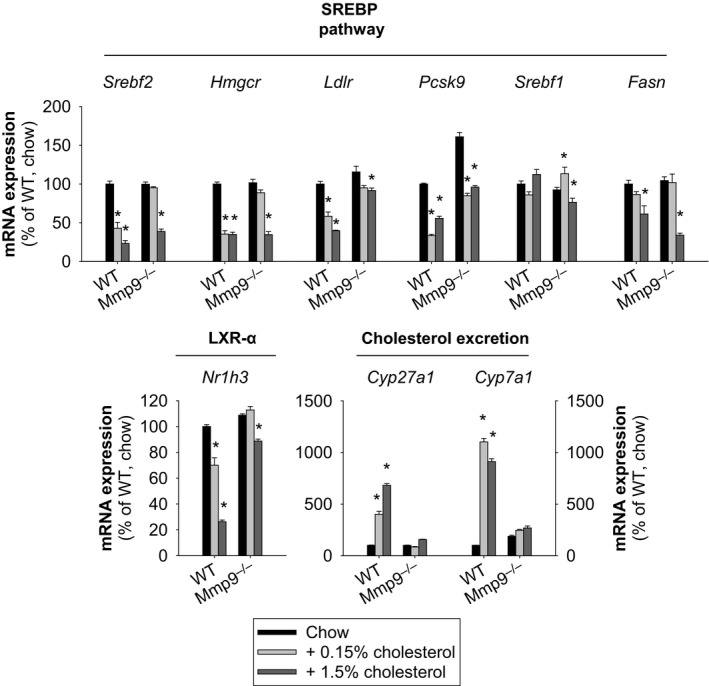
Impact of dietary cholesterol on hepatic transcriptional responses. Mice were fed either regular chow or chow supplemented with cholesterol (0.15% or 1.5%) for 2.5 days. Gene expression analysis was conducted at 0 and 2.5 days (n=4 to 5 mice per group [or treatment]). *P<0.05 vs normal chow for each genotype, all pairwise multiple comparisons vs control group (Holm–Sidak method), ANOVA. Cyp27a1 indicates sterol 27 hydroxylase; Cyp7a1, cholesterol 7 alpha hydroxylase; Fasn, fatty acid synthase; Hmgcr, 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methyl‐glutaryl‐coenzyme A reductase; Ldlr, low density lipoprotein receptor; LXR, liver X receptor; Mmp, matrix metalloproteinase gene; Nr1h3/LXR‐α, liver X receptor α; Pcsk9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; Srebf1, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1; Srebf2, gene for sterol regulatory element binding protein 2; SREBP, sterol regulatory element binding protein; WT, wild type.
