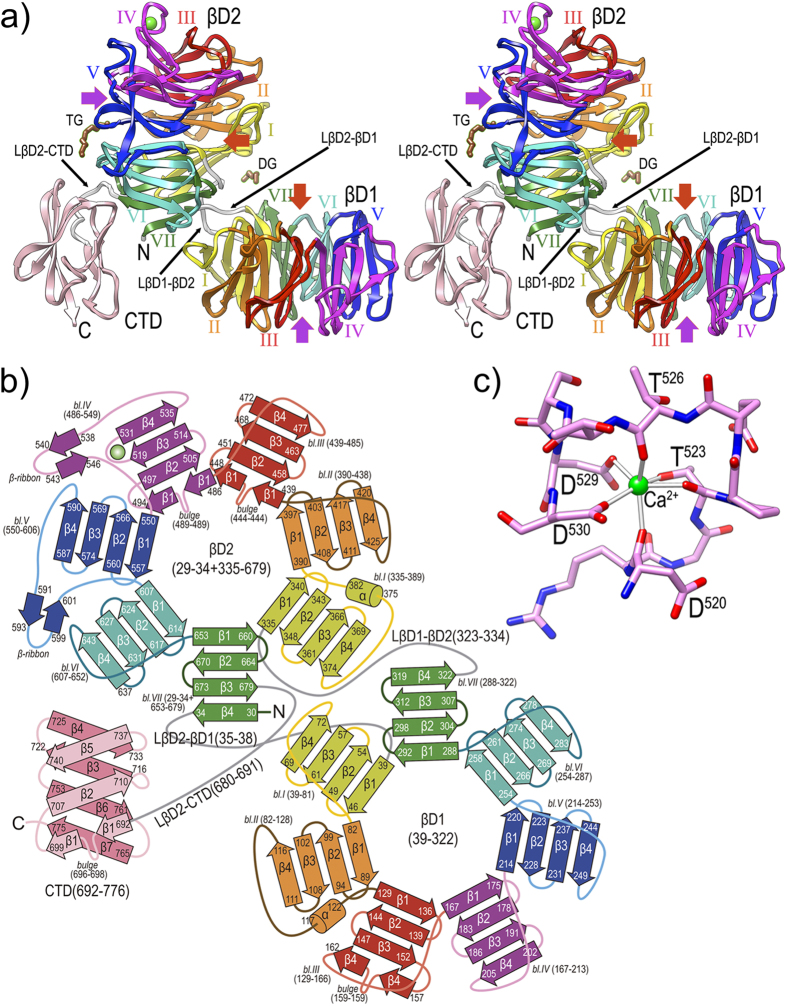
Figure 5. Overall crystal structure of PorZ.
(a) Ribbon-type plot in cross-eye stereo of the crystal structure to 2.9 Å resolution of PorZ depicting domains βD1, βD2 and CTD, and the three domain-connecting linkers (white ribbons; labeled LβD2-βD1, LβD1-βD2, and LβD2-CTD). Each of the seven blades of propellers βD1 and βD2 (labeled counter-clockwise I to VII) is colored in yellow, orange, red, magenta, blue, turquoise and green, respectively; the CTD is in pink. A structural calcium-binding site (green sphere) is found within βD1-blade IV, and a tetraethylene glycol (TG) and a diethylene glycol (DG) were tentaively assigned on the protein surface (brown stick-models). Other (functionally probably irrelevant) ions and ligands were omitted for clarity. The central shafts of βD1 and βD2 are pinpointed on the entry and exit sides of the propellers by red and purple arrows, respectively. For labels and extension of regular secondary structure elements, see (b). (b) Topology scheme of PorZ, with β-strands as arrows and helices as cylinders, colored as in (a). The polypeptide chain spans residues G29—R776 and the three constituting domains plus the linkers (in grey) are indicated with the residues delimiting each structural element (strands, bulges, helices, β-ribbons, blades and domains). The nomenclature adopted in the text for structure elements is “domain-blade-structural element”, e.g. βD1-VI-β3 or βD2-IV-β-ribbon. (c) Structural calcium-binding site framed by segment D520—D530 within loop Lβ3β4 of βD1-blade IV. The ion is octahedrally coordinated by D520O, T523O, T523Oγ, T526O, D529Oδ1 and D530Oδ1, which are at binding distances of ~2.4 Å.