Figure 7. Schematic of proposed molecular mechanism linking SPL activity, synaptic transmission and cognitive skills.
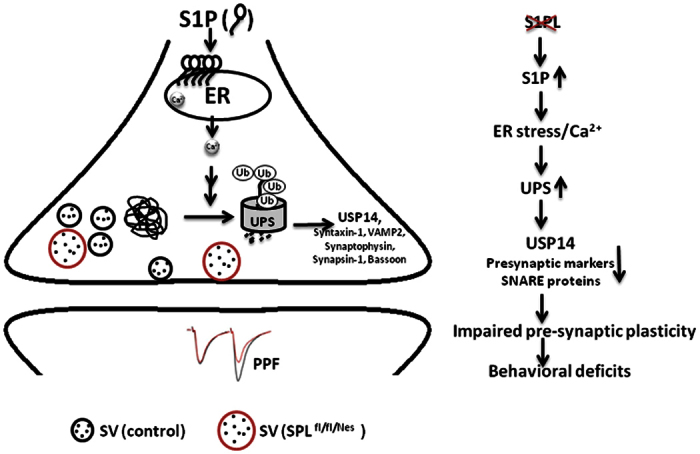
S1P accumulation upon SPL deletion causes elevation of cytosolic Ca2+, which in turn increases the activity of the ubiquitin-proteasomal system (UPS). As a consequence the expression of the proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme USP14 and of some presynaptic proteins is reduced, thereby impairing presynaptic plasticity coupled to behavioural and motor coordination deficits. PPF, paired pulse facilitation; SV, synaptic vesicle.
