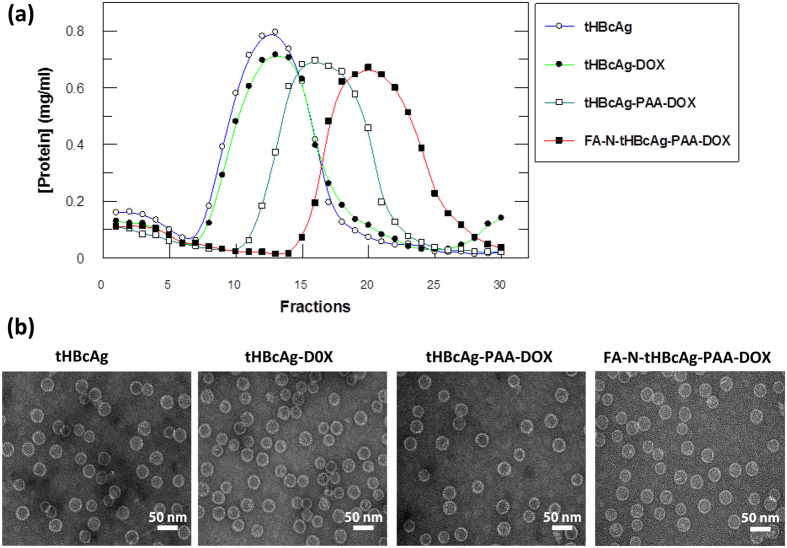
Figure 4. Packaging of doxorubicin by tHBcAg nanoparticles.
(a) Sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation of different tHBcAg nanoparticle packaging samples. tHBcAg nanoparticles containing doxorubicin (DOX) were separated by ultracentrifugation on sucrose gradients (8–40%). The total protein in each fraction (400 μL) was determined by a Bradford assay. Packaging of DOX with tHBcAg nanoparticles (tHBcAg-DOX), tHBcAg nanoparticles loaded with PAA-DOX (tHBcAg-PAA-DOX), and FA-conjugated tHBcAg nanoparticles using the nanoglue and loaded with PAA-DOX (FA-N-tHBcAg-PAA-DOX). tHBcAg nanoparticles (tHBcAg) were used as a negative control. (b) Electron micrographs of the tHBcAg nanoparticles from different packaging samples. The samples are labelled on top of the micrographs. All the samples assembled into spherical structures. White bars indicate 50 nm.