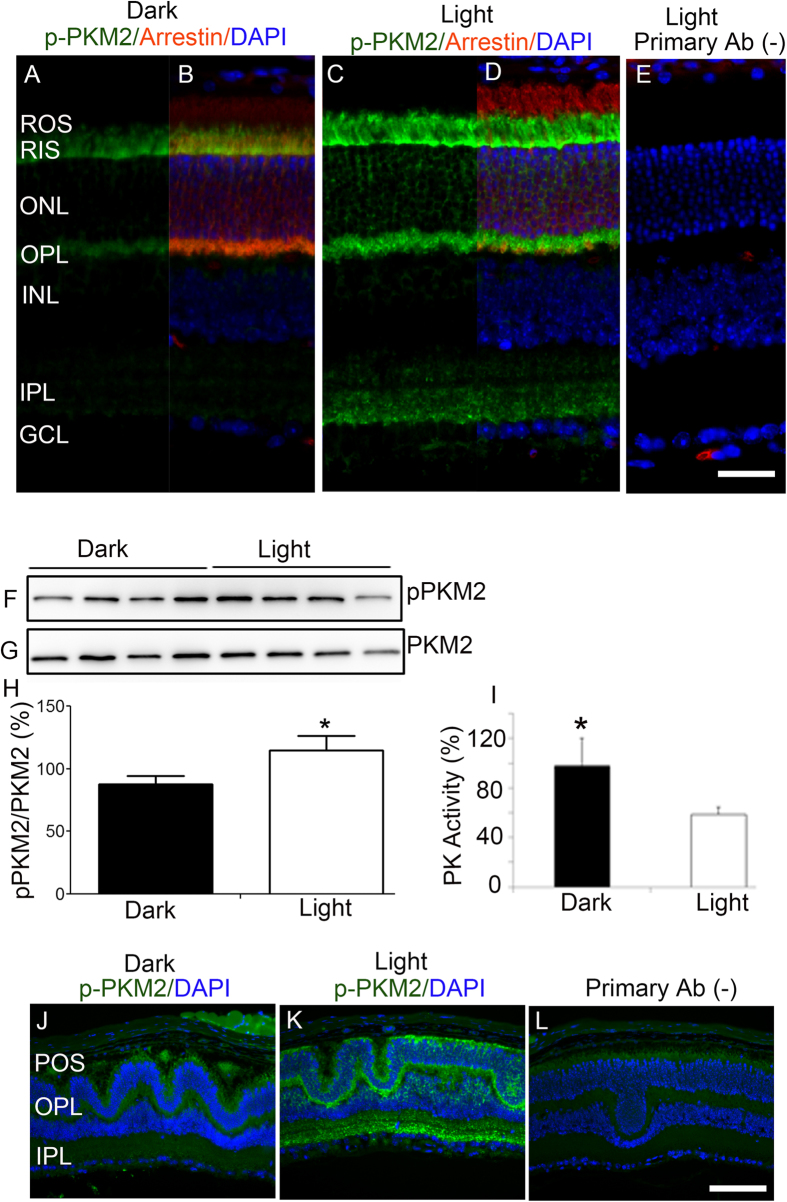
Figure 3. Light-dependent PKM2 phosphorylation in rod- and cone-dominant retinas.
Prefer-fixed sections of dark- (A,B) and light-adapted (C,D) mouse retinas were subjected to immunofluorescence with anti-p-PKM2 (Y105) (A,C), and anti-arrestin (B,D) antibodies. Panels (B,D) represent the merged images of p-PKM2 and arrestin, whereas panel (E) represents the omission of primary antibody. ROS, rod outer segments; RIS, rod inner segments; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Retinal lysates from dark- and light-adapted mice were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-pPKM2 (F) and anti-PKM2 (G) antibodies. Densitometric analysis of pPKM2 was performed in the linear range of detection, and absolute values were then normalized to PKM2 (H). Data are mean + SEM, n = 4. *p < 0.05. Pyruvate kinase activity was measured from dark- and light-adapted mouse retinas with an LDH-coupled enzyme assay. Data are mean ± SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05. Prefer-fixed sections of dark- (J) and light-adapted (K) Nrl−/− mouse retinas were subjected to immunofluorescence with anti-pPKM2 (J,K). Panel (L) represents the omission of primary antibody. POS, photoreceptor outer segments; OPL, outer plexiform; IPL, inner plexiform layer. Scale bar 50 μm. Full-length blots are presented in the Supplementary Information.