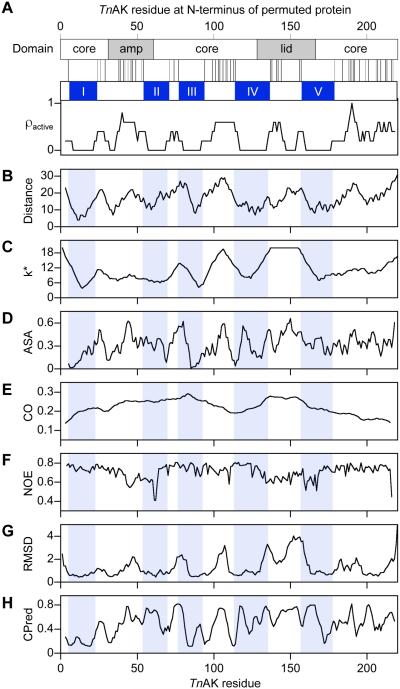
Figure 3.
Relationship between AK structure and the pattern of permutation tolerance. (A) A comparison of AK domain structure with the peptide bonds that can be broken by permutation without disrupting TnAK function reveals five contiguous peptides that lack fission sites, I-V. The dispersion of tolerated backbone fragmentation sites (ρactive) was calculated using a sliding window of five residues. For all residues within TnAK, profiles were generated that show: (B) the distance of each αC to the γ-Pi of Ap5A, (C) k*, the number of unique amino acids in a sequence alignment of 100 AK orthologs, (D) the accessible surface area, (E) the relative contact orders of permuted variants that begin with that residue, (F) the NOE values, (G) the positional structural deviation calculated from 45 pairwise superpositions of Ap5A-bound AK orthologs, and (H) the CPred scores.