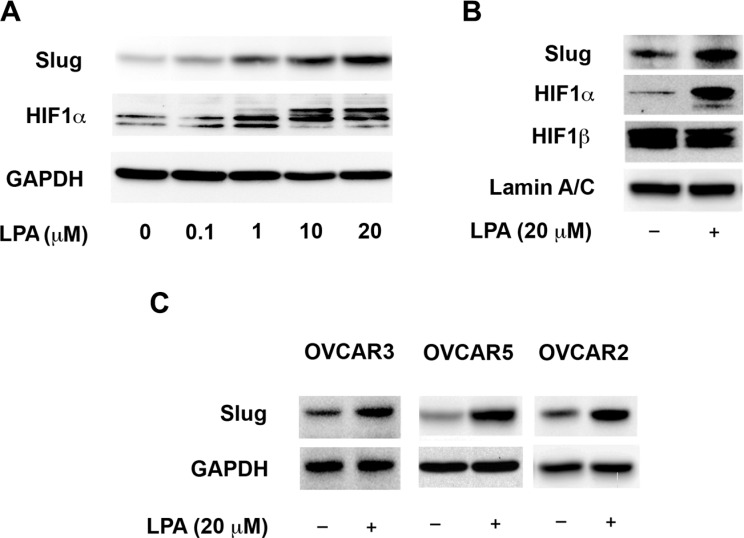
Figure 3. LPA-signaling activates the transcription factors Slug and HIF1α.
(A) HIF1α- and Slug-levels shows a dose-dependent response to LPA stimulation. SKOV3.IP cells were serum starved overnight and then stimulated with the indicated levels of LPA for 4 hours. Cells were lysed and the levels of HIF1α and Slug in the lysates were analyzed by immunoblot analysis using the respective antibodies. The blot was stripped probed with GAPDH-antibodies to monitor equal loading of proteins. (B) LPA stimulates the nuclear localization of HIF1α and Slug. SKOV3.IP cells were serum starved overnight and then treated with 20 μM of LPA for 4 hours along with untreated control. Nuclear extracts derived from these cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies specific to Slug, HIF1α and HIF1β. Levels of Lamin A/C were used as a marker for nuclear compartment and loading control for equal protein loading in each lane. (C) LPA-stimulated increase in the expression of Slug is cell-type independent. OVCAR3, OVCAR5 an OVCAR2 cells were serum-starved overnight and then treated with 20 μM of LPA for 4 hours. Expression levels of Slug Lysates derived from these cells were analyzed for the expression levels of Slug by immunoblot analysis using antibodies for Slug. Levels of GAPDH were analyzed in the stripped blot to ensure equal loading of proteins. (n = 3).