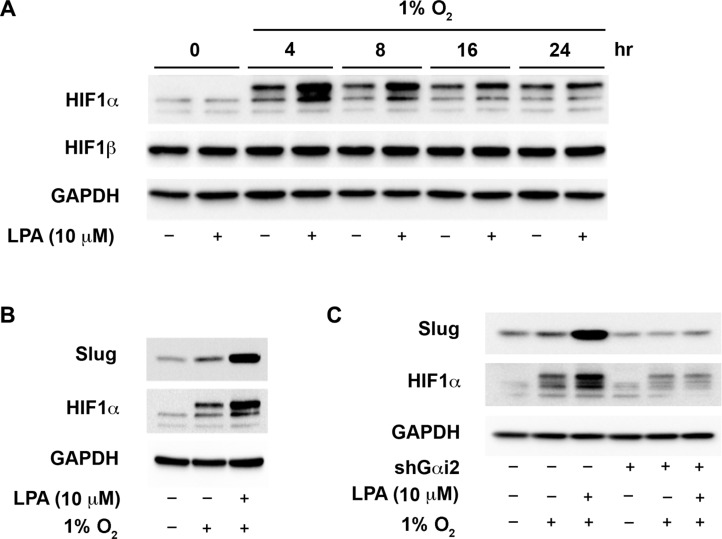
Figure 5. Gαi2 stimulates an increase in the levels of HIF1α in hypoxia.
(A) LPA enhances the up-regulation of HIF1α in hypoxia. SKOV3.ip cells were incubated in a hypoxic chamber containing 1% O2 and stimulated with 20 μM of LPA for the indicated lengths of time. Lysates from these cells were analyzed for the levels of HIF1α by immunoblot analysis using the antibodies to HIF1α. The blot was stripped and probed with antibodies to HIF1β and GAPDH to monitor their respective levels. The levels of GAPDH were used to monitor equal loading of proteins. (B) LPA enhances hypoxia-mediated increase in Slug levels. SKOV3.ip cells were serum-starved overnight. The control group was left in normoxic conditions while the hypoxia and the hypoxia plus LPA-stimulated cells (20 μM of LPA) were put into the hypoxic chamber (1% O2) for 4 hours in serum-free medium. Lysates from these cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the antibodies to Slug. GAPDH was probed in the stripped blot to ensure equal loading of proteins in each lane (C) Gαi2 is required for the increased expression of HIF1α and Slug in hypoxia. SKOV3.ip cells with either non-sense shRNA or with shRNA that targeted Gαi2 were placed in hypoxic chamber along with normoxic control group. Cells under hypoxia were stimulated with 10 μM of LPA for 4 hours. Lysates derived from these cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies to HIF1α and Slug. Levels of GAPDH in the stripped blot were monitored to ensure equal loading of the proteins in each lane. Profile from a representative experiment is presented in each panel (n = 3).