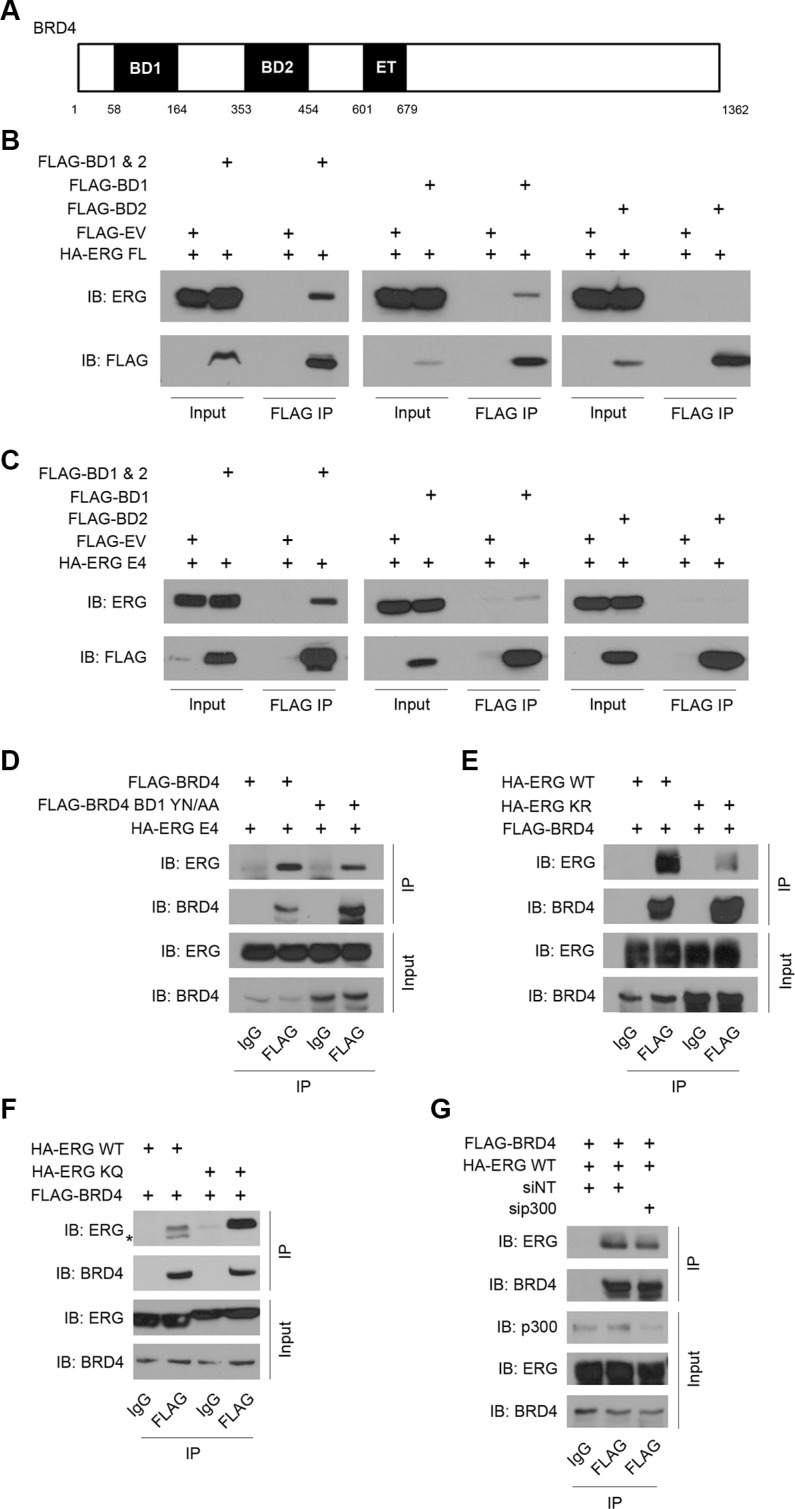
Figure 2. Bromodomain-1 of BRD4 and 96KGGK99 of ERG are important for interaction.
(A) Schematic showing known domains for BRD4, notably the two conserved bromodomains (BD1 and BD2) and the extraterminal (ET) domain. (B) Western blot showing FLAG co-IP with over-expressed FLAG-tagged full-length BRD4 or truncations and HA-tagged full-length ERG in HEK293T cells. FLAG co-IP in cells transfected with FLAG empty vector (EV) as a control. (C) Western blot showing FLAG co-IP with over-expressed FLAG-BRD4 or truncations and HA-ERG T1-E4 in HEK293T cells. FLAG co-IP in cells transfected with FLAG empty vector as a control. (D) Western blot showing FLAG co-IP with over-expressed FLAG-BRD4 or FLAG-BRD4 with mutated BD1 and HA-ERG T1-E4 in HEK293T cells. IgG co-IP as a control. (E) Western blot showing FLAG co-IP with over-expressed FLAG-BRD4 and HA-ERG full-length wild-type or acetylation-block mutant (KR) in HEK293T cells. IgG co-IP as a control. (F) Western blot showing FLAG co-IP with over-expressed FLAG-BRD4 and HA-ERG full-length wild-type or acetylation-mimic mutant (KQ) in HEK293T cells. IgG co-IP as a control. *Non-specific band. (G) Western blot showing FLAG co-IP with over-expressed FLAG-BRD4 and HA-ERG full-length wild-type with or without p300 knockdown in HEK293T cells. IgG co-IP as a control.