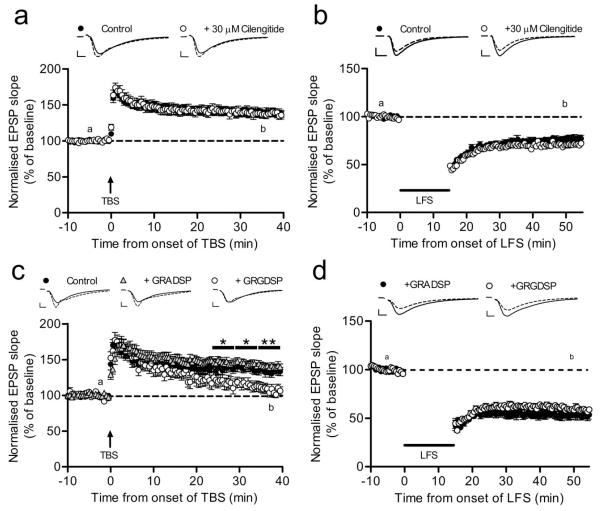
Figure 3.
Cilengitide does not affect LTP or LTD whereas synthetic RGD peptide affects LTP stabilization. (a, b) Cilengitide (30 μM) has no effect on the induction and maintenance of TBS-induced LTP or LFS-induced LTD in acute hippocampal slices [LTP: cilengitide (n = 6, 11) vs. control (n = 6, 11); LTD: cilengitide (n = 5, 14) vs. control (n = 5, 12)]. (c) Disrupting RGD-sensitive integrin-ECM interactions in acute hippocampal slices by 500 μM GRGDSP slowly reverses potentiation to baseline [control (n = 7, 10), GRADSP (n = 4, 12), GRGDSP (n = 7, 8), two-way repeated-measures ANOVA; (control vs GRGDSP): t25-29.5: F1,16 = 4.87; P = 0.0423; t30-34.5: F1,16 = 7.73; P = 0.0134; t35-39.5: F1,16 = 9.95; P = 0.0061]. (d) GRGDSP (500 μM) has no effect on LTD in acute hippocampal slices [GRADSP (n = 8, 12), GRGDSP (n = 8, 12)]. Representative traces are from time points “a” (solid) and “b” (dashed). Scale bars: (a-d) = 5 ms, 0.5 mV. Error bars are ±s.e.m.