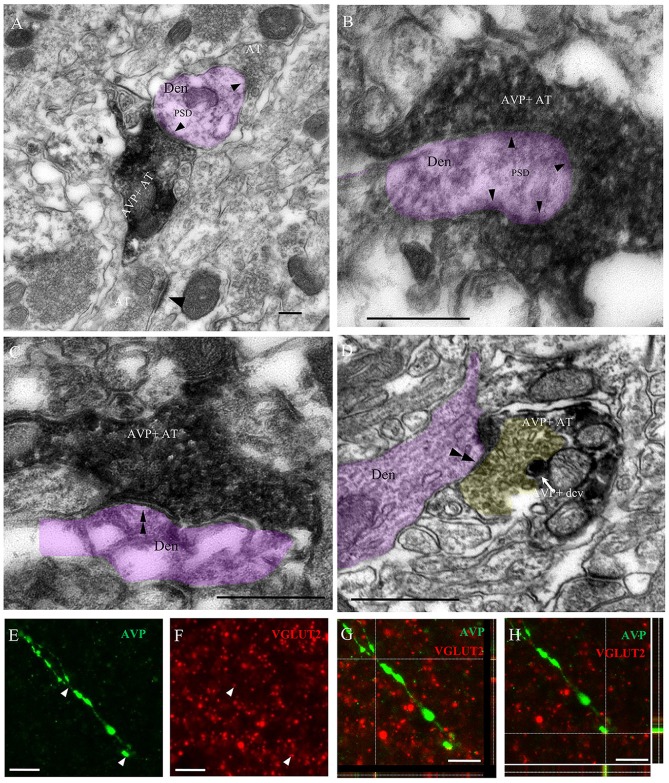
Figure 4.
Immuno-electron microscopical evidence of synaptic innervation by thick and thin AVP-containing fibers onto central amygdala (CeA) neurons, establishing either Gray type I (asymmetric; thick) or Gray type II (symmetric; thin) synapses. Examples of thick axon terminals (AT) (A,B) making Gray type I synapses (the presence of postsynaptic density, PSD, are indicated by single arrowheads) and thin AT (C,D) making Gray type II synapses (the absence of PSD are indicated by double arrowhead) onto CeA neurons’ dendrites (Den, pink shaded). Note that the yellow shaded presynaptic active zone of an axon terminal of a thin fiber contained pleomorphic small clear vesicles, which is a remarkable feature of a GABAergic AT; it also contained AVPir+ dense core vesicle (dcv). Thick AVPir fibers in the CeA contain vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT2)-positive varicosities. Confocal microscopy analysis of CeA showed thick varicose fibers immunopositive for AVP (E) and multiple VGLUT2-positive terminals (F) with co-expression of VGLUT2 and AVP in a representative thick fiber (G,H). For (G,H), the x–y (center), x–z (box below) and y–z (right box) images are shown. Scale bars: (A–D) 500 nm; (E–H) 10 μm.