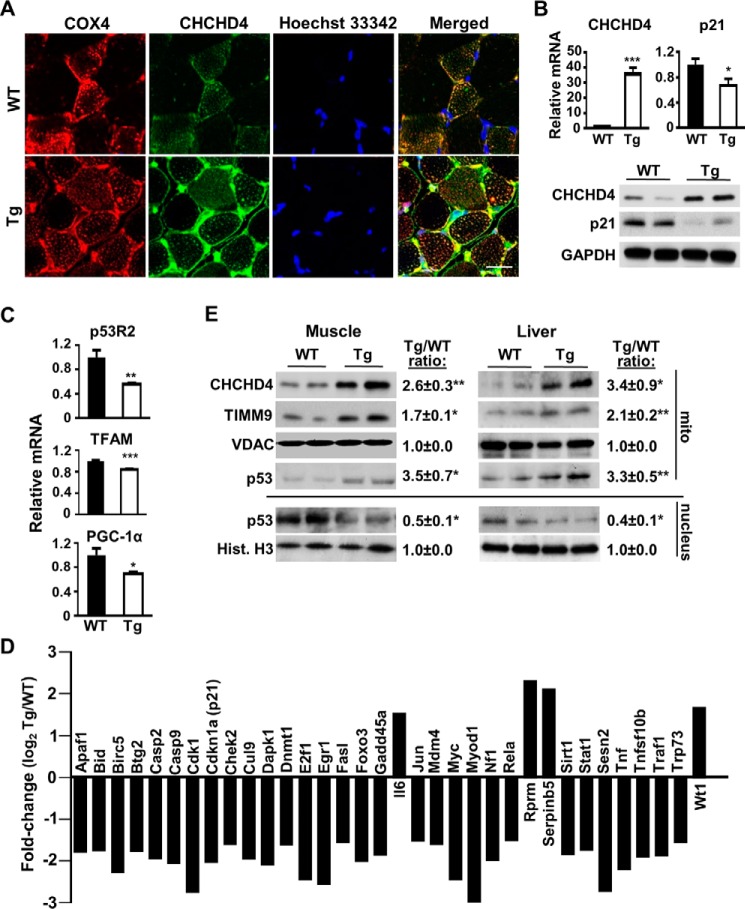
FIGURE 1.
CHCHD4 regulates p53 subcellular localization and nuclear activity in vivo. A, confocal immunofluorescence images of CHCHD4 (green) expression in cross-sections of skeletal muscle of WT and CHCHD4 Tg mice. Immunofluorescence labeling of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 (COX4) (red) and Hoechst 33342 (blue) staining served as mitochondrial and nuclear markers, respectively. B, mRNA and protein expression of CHCHD4 and p21 in skeletal muscle of WT and CHCHD4 Tg mice. n ≥ 4. C, mRNA expression of p53-regulated mitochondrial biogenesis genes in skeletal muscle of WT and CHCHD4 Tg mice. n ≥ 4. D, relative mRNA expression (Tg versus WT) of p53-regulated genes analyzed by screening RT-PCR array in skeletal muscle. n ≥ 4. E, comparison of p53 protein in the mitochondrial (mito) and nuclear fractions of skeletal muscle and liver of WT and CHCHD4 Tg mice treated with doxorubicin for 18 h. VDAC and histone H3 (Hist. H3) served as mitochondrial and nuclear protein loading controls, respectively. Shown is a representative immunoblot image of four independent experiments used for quantification. Values are mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Scale bar = 20 μm.