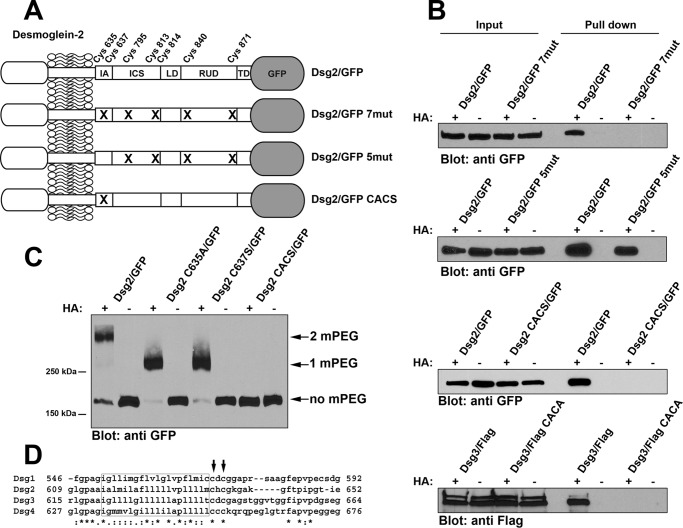
FIGURE 1.
Cysteine residues in the IA domain of Dsg2 and Dsg3 are palmitoylated. A, the relative location of the seven cysteine residues present in the cytoplasmic tail of Dsg2. The extracellular domain of the Dsg2 is not shown in detail. Dsg2/GFP is wild-type full-length Dsg2 with monomeric GFP fused to the carboxyl terminus. Dsg2/GFP 7mut has all seven cysteine residues mutated. Dsg2/GFP 5mut retains Cys-635 and Cys-637 but has the five distal cysteines mutated. Dsg2/GFP CACS contains only the mutations C635A and C637S. IA, intracellular anchor; LD, linker domain; RUD, repeat unit domain; TD, terminal domain. B, A431 cells stably expressing wild-type Dsg2/GFP and the various mutant Dsg2/GFP were analyzed using the acyl biotin exchange assay. 10% of the input lysate used for each pulldown was loaded (left). Streptavidin-agarose pulldowns of biotin-labeled proteins were also loaded (right). Immunoblot analysis was performed using anti-GFP (JL-8) to detect Dsg2/GFP fusion proteins and anti-FLAG to detect FLAG-tagged Dsg3. C, A431 cells stably expressing wild-type Dsg2/GFP or various point mutants (Dsg2 C635A/GFP, Dsg2 C637S/GFP, and Dsg2/GFP CACS) were analyzed by mass tag labeling. Immunoblot analysis was performed using anti-GFP (JL-8) to detect Dsg2/GFP fusion proteins. The arrows indicate the bands migrating at the expected molecular weight for the incorporation of two mPEG, one mPEG, or no mPEG moieties. Acyl biotin exchange assays and mass tag labeling assays were repeated three times using independent cell cultures for each experiment. D, amino acid sequence alignment of the four human Dsg proteins. The predicted transmembrane segments are boxed, and the cysteine residues corresponding to Cys-635 and Cys-637 of Dsg2 are indicated by arrows.