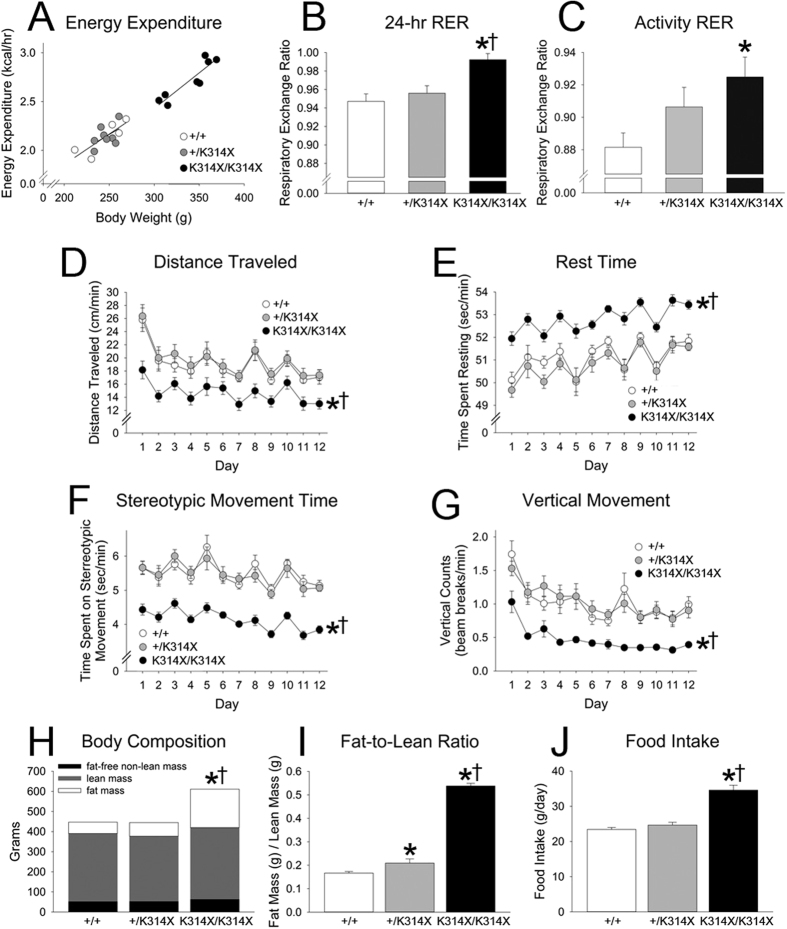
Figure 1. Effects of Mc4rK314X mutation on energy expenditure, physical activity, body composition, and food intake in male rats.
(A) When body weight is taken into account using covariance, no difference is seen between genotypes in energy expenditure. (B) Respiratory exchange ratio (RER, VCO2/VO2), an indicator of substrate use, was significantly higher in rats lacking functional MC4R (Mc4rK314X/K314X) compared to wild-type (Mc4r+/+) rats or rats heterozygous for the allele (Mc4r+/K314X) during 24-hr calorimetry. (C) During the first 10 min of controlled treadmill activity after short-term food restriction, RER of Mc4rK314X/K314X rats was higher than Mc4r+/+ rats’ RER, indicating a lower reliance on lipids compared to Mc4r+/+ rats. Over the course of 12 days in activity monitors, Mc4rK314X/K314X rats (n = 8) showed consistently suppressed physical activity, including (D) distance traveled, (E) time spent resting, (F) stereotypic movements (e.g., grooming), and (G) vertical movements (e.g., rearing). (H) Mc4rK314X/K314X rats were significantly heavier than either Mc4r+/+ (n = 8) or Mc4r+/K314X rats (n = 8), primarily because of fat mass. (I) While Mc4r+/K314X and Mc4r+/+ rats did not differ in body weight, Mc4r+/K314X rats had a moderately but significantly greater fat-to-lean ratio. (J) Mc4rK314X/K314X rats showed greater daily energy intake; Mc4r+/K314X and Mc4r+/+ rats did not differ from each other in food intake. *significantly different from Mc4r+/+; †significantly different from Mc4r+/K314X; p < 0.05. For all calorimetry, n = 8 Mc4rK314X/K314X, n = 8 Mc4r+/K314X, n = 6 Mc4r+/+; For all other measures, n = 8 Mc4rK314X/K314X, n = 8 Mc4r+/K314X, n = 8 Mc4r+/+.