Figure 2. ELISA was used to measure plasma levels of carbamoyl-phosphate synthase I (CPSI) in CHD-PAH/CHD patients (n = 145) and controls (n = 37).
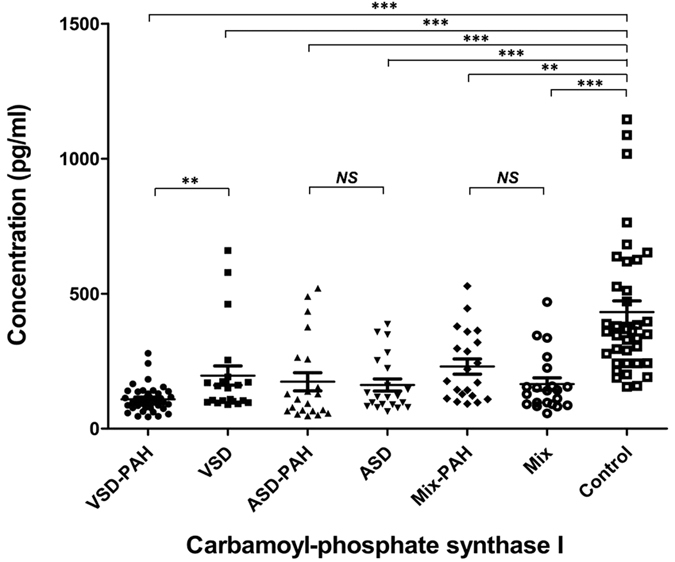
Plasma CPSI levels in patients with VSD-PAH (109.2 ± 7.718 pg/ml, n = 40; P = 0.000 by ANOVA compared with control group) and VSD (196.5 ± 35.68 pg/ml, n = 21; P = 0.000 by ANOVA compared with control group) were lower than that in the healthy controls (431.8 ± 41.42 pg/ml, n = 37). The plasma CPSI level in ASD-PAH patients (173.7 ± 33.58 pg/ml, n = 21; P < 0.0001 by unpaired t test) and ASD patients (161.9 ± 22.51 pg/ml, n = 21; P = 0.000 by ANOVA compared with control group) was significantly lower than that in normal controls (431.8 ± 41.42 pg/ml, n = 37). The plasma CPSI level in Mix-PAH patients (230.1 ± 28.18 pg/ml, n = 21; P = 0.000 by ANOVA compared with control group) and Mix patients (165.0 ± 23.17 pg/ml, n = 21; P = 0.000 by ANOVA test compared with control group) was significantly lower than that in normal controls (431.8 ± 41.42 pg/ml, n = 37). Data are shown as mean ± SEM.
