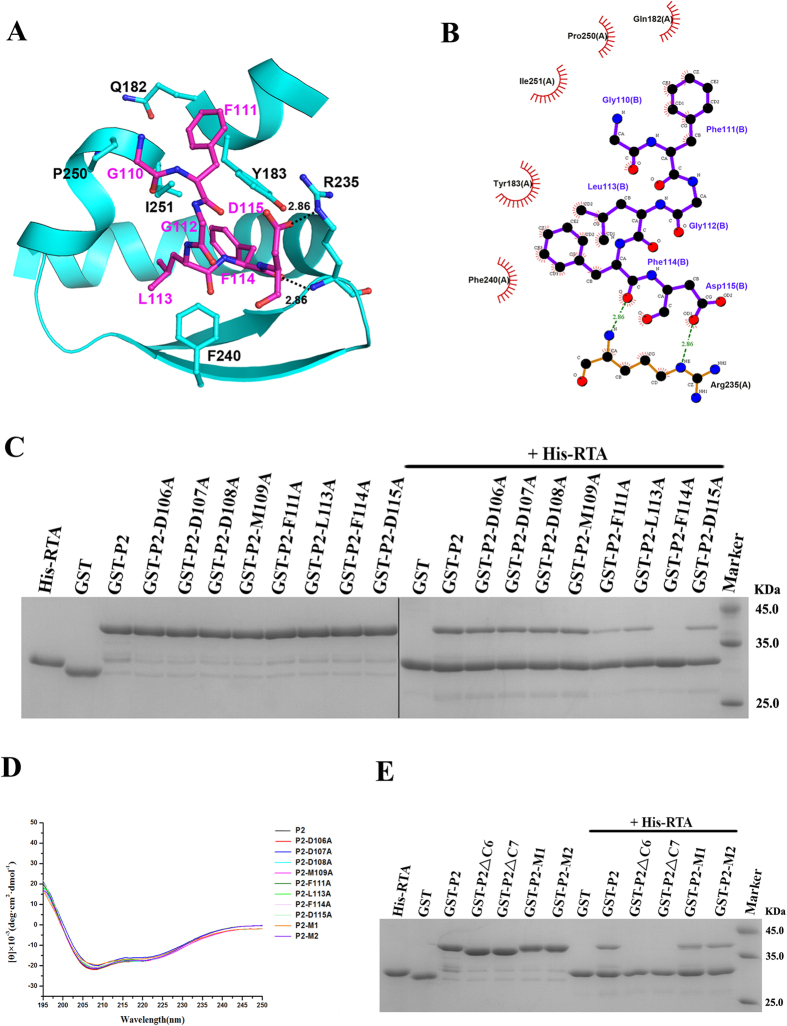
Figure 3. Validation of the residues in the C10-P2 peptide that are responsible for the interaction with RTA.
(A) A cartoon representation of the binding interface between RTA (cyan) and the C10-P2 peptide (magenta); residues involved in the interaction are labelled and shown as sticks, and hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines. (B) Ligplot analysis of the interaction between RTA and the C10-P2 peptide. (C) Interaction between RTA and the P2 variants as assessed by pull-down assay. His-RTA, GST, GST-P2, and GST-P2 variants were used as controls. GST-P2-F111A, GST-P2-L113A and GST-P2-D115A showed decreased binding with His-RTA. GST-P2-F114A completely lost the ability to associate with His-RTA. (D) CD spectra of recombinant P2 and the P2 mutants. (E) The interaction between RTA and the conserved DDDM motif of C10-P2, as assessed by pull-down assay. His-RTA, GST, GST-P2, GST-P2ΔC6 (in which the 6 C-terminal residues were deleted), GST-P2ΔC7 (in which the 7 C-terminal residues were deleted), GST-P2-M1 (in which residues DDD were mutated to AAA) and GST-P2-M2 (in which residues DDDM were mutated to AAAA) were used as controls.