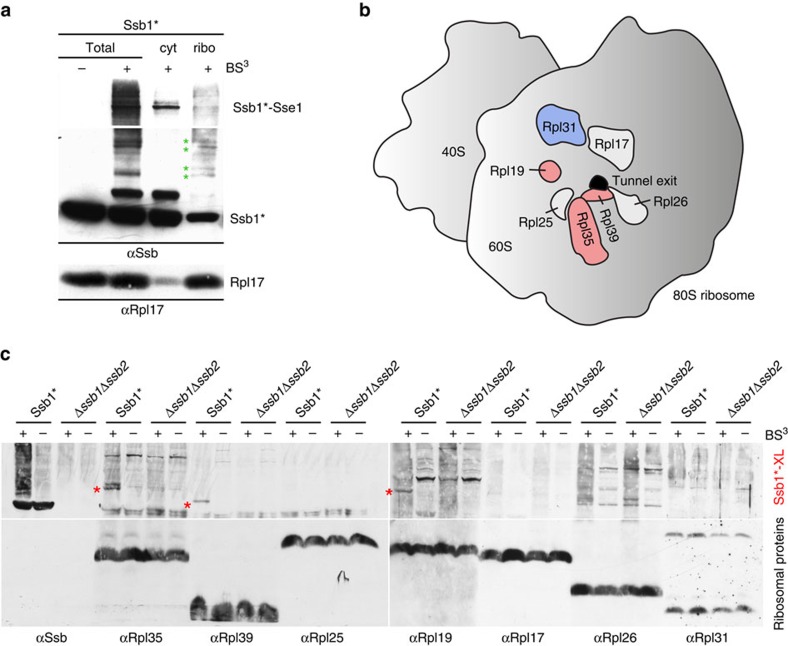
Figure 1. Ssb contacts ribosomal proteins at the tunnel exit.
(a) Ssb is crosslinked to proteins of the large ribosomal subunit. Isolated ribosomes of the Ssb1* strain were incubated with (+) or without (−) the crosslinker BS3. The crosslinked sample (Total) was separated into a cytosolic supernatant (cyt) and a ribosomal pellet (ribo) via centrifugation through a low-salt sucrose cushion and was analysed via immunoblotting with αSsb. Shown is a short exposure of the upper part of the blot (>116 kDa), which contains the strong crosslink between Ssb1* and Sse1 (Ssb1*–Sse1) and a long exposure of the lower part of the blot (<116 kDa), which contains the weaker crosslinks between Ssb1* and ribosomal proteins (green asterisks). Rpl17 served as a marker for the ribosomal fraction. (b) Schematic representation of selected ribosomal proteins (Rpl19, Rpl35 and Rpl39 in pink; Rpl31 in blue; Rpl17, Rpl25 and Rpl26 in white) surrounding the tunnel exit (black) of the yeast ribosomal large subunit (grey). (c) Identification of ribosomal proteins crosslinked to Ssb1*. Crosslinking was performed in total cell extract of Ssb1* or Δssb1Δssb2 strains. Aliquots were analysed via immunoblotting using αSsb, αRpl35, αRpl39, αRpl25, αRpl19, αRpl17, αRpl26 and αRpl31 as indicated. Crosslink products between Ssb1* and ribosomal proteins (Ssb1*-XL) are indicated with red asterisks.