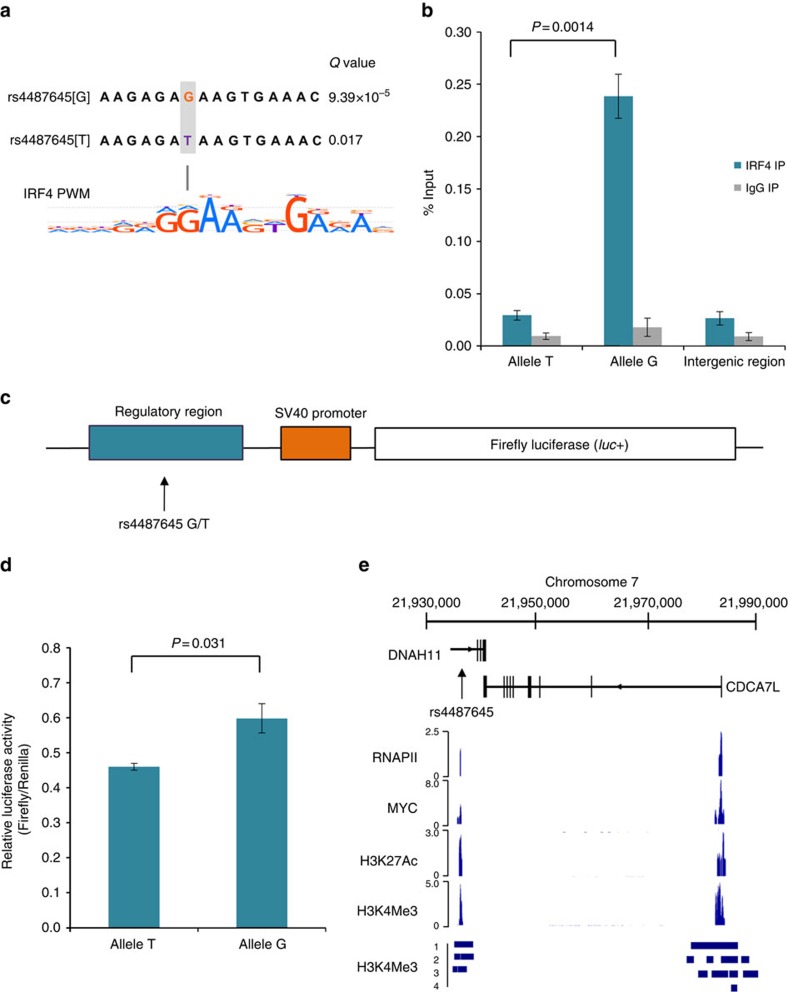
Figure 2. SNP rs4487645 shows allele-specific binding of IRF4 and confers enhancer regulatory activity in multiple myeloma cells.
(a) rs4487645 is located in an IRF4 DNA-binding motif predicted by Find Individual Motif Occurrences (FIMO). Shown below is the IRF4 position weight matrix generated by HOCOMOCO. G-risk allele is highlighted in red. (b) ChIP–qPCR using either the anti-IRF4 or isotype control antibody was performed on GM11992 heterozygous for rs4487645. The ChIP–qPCR signal is based on the abundance of allele-specific amplicons for rs4487645 in the immunoprecipitated DNA, relative to input DNA. Also shown is the relative abundance of intergenic control region. ChIP data show differential binding of IRF4 for the risk G-allele relative to the T-allele. Data shown are mean±s.e.m. from three biological replicates and assessed by two-tailed t-test. Each qPCR reaction was performed with three technical replicates. (c) An ∼1 kb putative regulatory sequence flanking rs4487645 (G/T) was cloned upstream of the SV40 promoter in the pGL3-promoter vector for testing luciferase reporter gene activity. (d) The resultant reporter constructs were transiently transfected into KMS11, and the relative luciferase activity was measured for each reporter gene construct. The luminescence ratio of the experimental vector to the Renilla internal control, pRL-SV40, was normalized to the backbone pGL3-SV40 promoter vector. Data shown are mean±s.e.m. from four biological replicates and assessed by two-tailed t-test. (e) The chromatin state of the DNAH11–CDCA7L gene locus is detailed with RNA polymerase II (RNAPII), MYC, H3K4Me3 and H3K27Ac ChIP-seq data from MM cell line MM1.S (GSE36354). ChIP-seq data in four MM patients (labelled 1–4) show MM-unique H3K4Me3-occupied regions compared with normal bone marrow plasma cells (GSE53215).