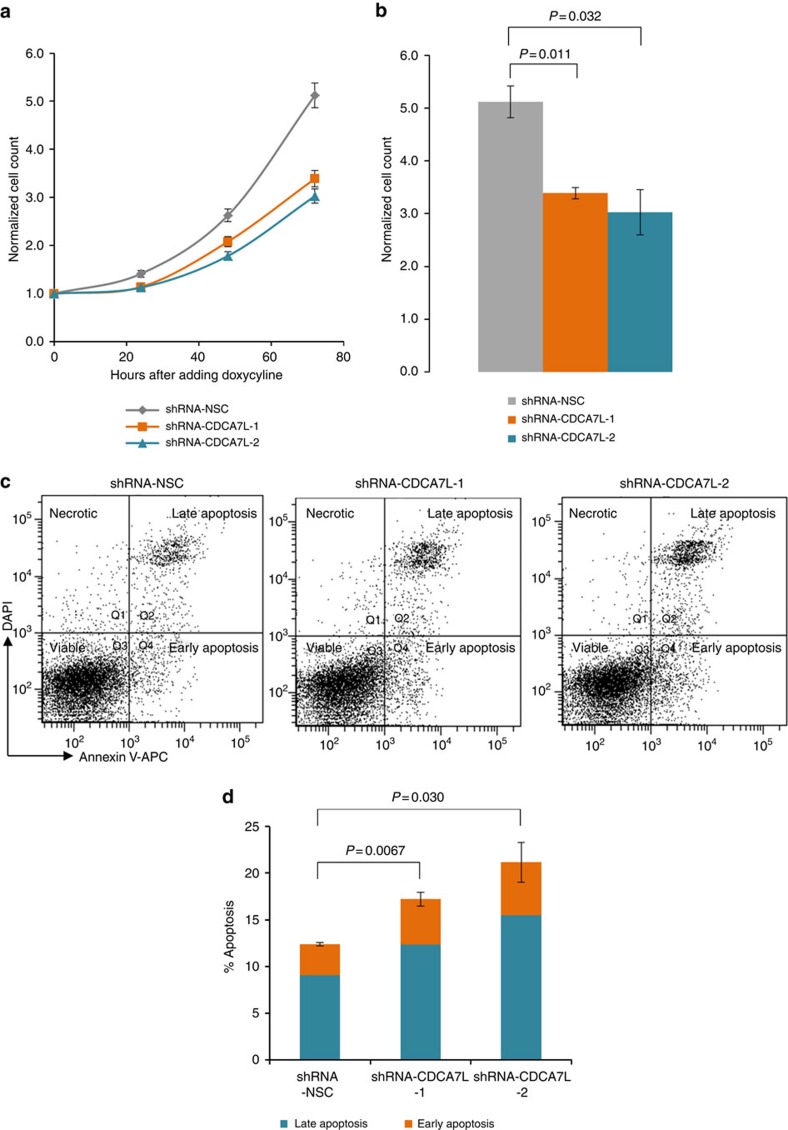
Figure 4. CDCA7L knockdown induces cell apoptosis and suppresses cellular proliferation.
(a) Data shown are the mean cell counts of viable Trypan-blue-negative cells±s.e.m. for three biological replicates at 24, 48 and 72 h after addition of doxycycline (final concentration 1 μg ml−1). Data were normalized to initial seeding number at 0 h when doxycycline was added to cells. (b) P values assessing the differences in normalized cell counts between CDCA7L and control knockdowns at 72 h were determined using two-tailed t-test. (c) Cell viability at 72 h after addition of doxycycline was assessed with FACS using Annexin V-APC and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting data show four subgroups of cells: the lower left quadrant (Q3; unstained) represents the viable cell population; the lower right (Q4; Annexin V-APC+ DAPI−) contains early apoptotic cells; the upper right quadrant (Q2; Annexin V-APC+ DAPI+) represents late apoptotic cells; the upper left (Q1; Annexin V-APC− DAPI+) represents necrotic cells. (d) The percentages of apoptotic cells of shRNA-CDCA7L-1, shRNA-CDCA7L-2 and shRNA-NSC are shown at 72 h after addition of doxycycline. Data shown are mean±s.e.m. for three biological replicates. P values were determined with two-tailed t-test.