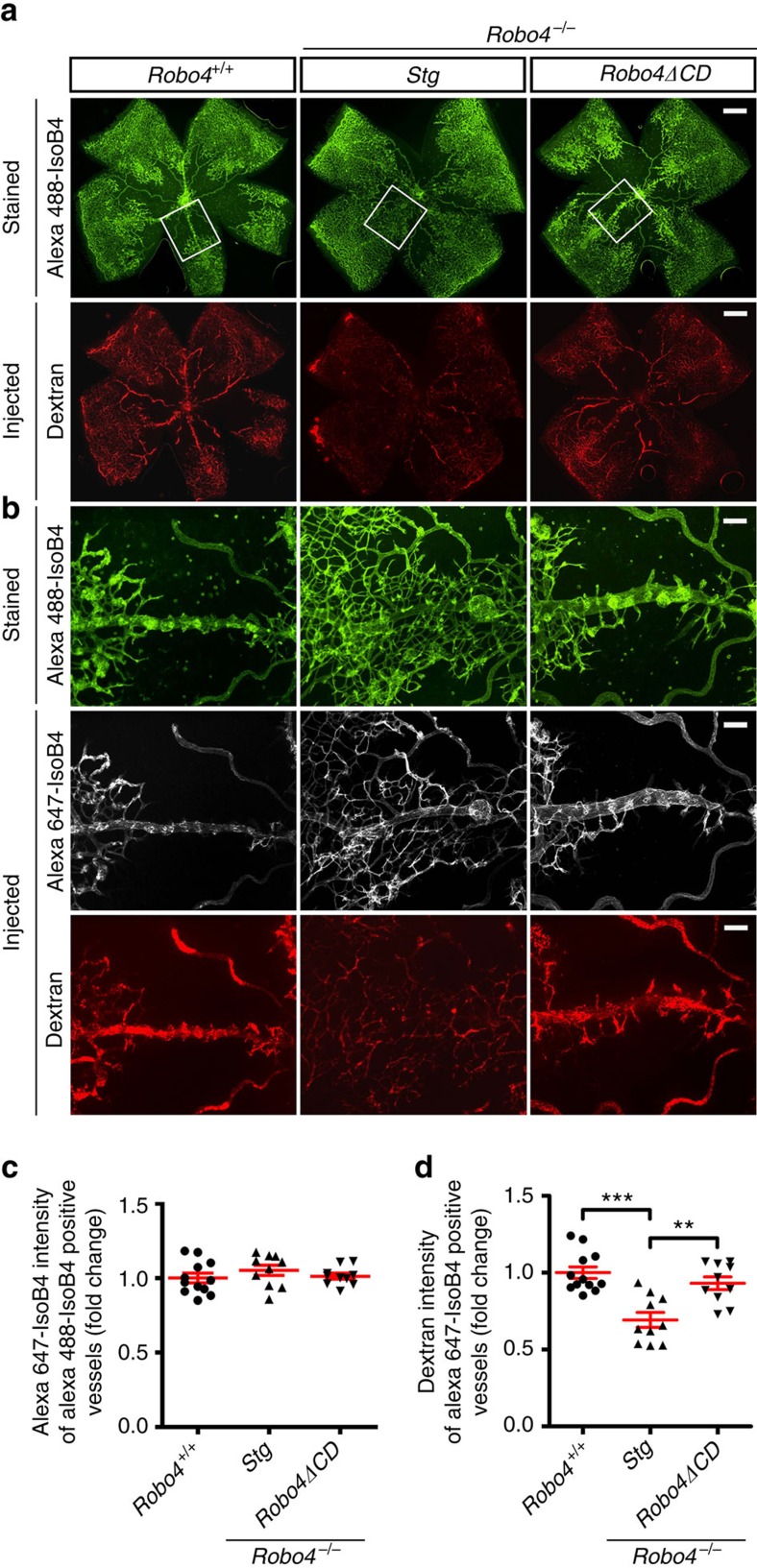
Figure 3. Robo4ΔCD inhibits OIR retinal vessel leakage.
P17 OIR mice of the indicated genotypes were injected with Rhodamine-dextran and Alexa 647-IsoB4 for 5 min, then mice were sacrificed and vasculature was stained with Alexa 488-IsoB4. (a) Low-magnification images of the Alexa 488-IsoB4-stained vasculature (upper panel, green) and Rhodamin-dextran perfusion (red, lower panel). Note reduced intensity of dextran labelling indicating increased permeability in Robo4−/−;Stg mice compared with Robo4+/+ and Robo4−/−;Robo4ΔCD mice. Scale bars, 500 μm. (b) Higher magnification images of the boxed areas in a. Upper panel: Alexa 488-IsoB4-stained vasculature. Middle panel: injected Alexa 647-IsoB4-labelled vasculature. Lower panel: injected rhodamine-dextran labelled vasculature. Scale bars, 100 μm. (c) Quantifications of injected Alexa 647-IsoB4 fluorescence intensity in Alexa 488-IsoB4-labelled vasculature in images shown in b. Each dot represents a retina. N=10–12 retinas (5–6 mice) per group. Error bars represent s.e.m. Note no significant difference between genotypes, indicating equal perfusion of all groups. (d) Quantification of dextran fluorescence intensity in Alexa 647-IsoB4-labelled vasculature. Data were normalized to Alexa 647-IsoB4 intensity and are presented as fold change compared with Robo4+/+ mice. Robo4−/−;Stg mice show reduced intensity of dextran labelling hence increased leakage, this is rescued in Robo4−/−;Robo4ΔCD mice. Each dot represents a retina. N=10–12 retinas (5–6 mice) per group. Error bars represent s.e.m. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001, Mann–Whitney U test.