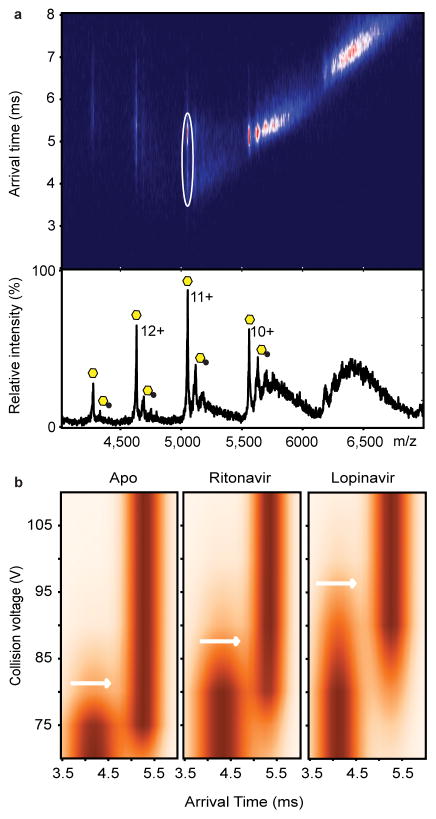
Figure 4.
Collision-induced unfolding reveals differences in the unfolding trajectories of free ZMPSTE24 compared with its drug-bound states. (A) Mass spectrum and arrival times of ZMPSTE24 acquired under collisional activation (80 V) (upper panel) in the presence of ritonavir in C8E4. The arrival time distribution of the 11+ charge state is consistent with partial unfolding of the enzyme, whereas charge states 10+ and 9+ remain compact, consistent with native-like structure in the gas phase. Peaks assigned to binding of the drug are labelled with black circles. The 11+ charge states of apo and the ZMPSTE24 ritonavir complex, selected for collision induced unfolding measurements, are shown in the ion mobility data (white circle). Native and intermediate states are apparent at this voltage (80 V). (B) Comparison of the collision-induced unfolding from 70 V to 110 V of the 11+ charge state of Zn2+-bound ZMPSTE24 with unfolding in the presence of ritonavir or lopinavir. The transition from compact folded state to the first intermediate state is highlighted (white arrows). This transition occurs at a higher voltage for lopinavir-bound ZMPSTE24 than for the ritonavir-bound ZMPSTE24.