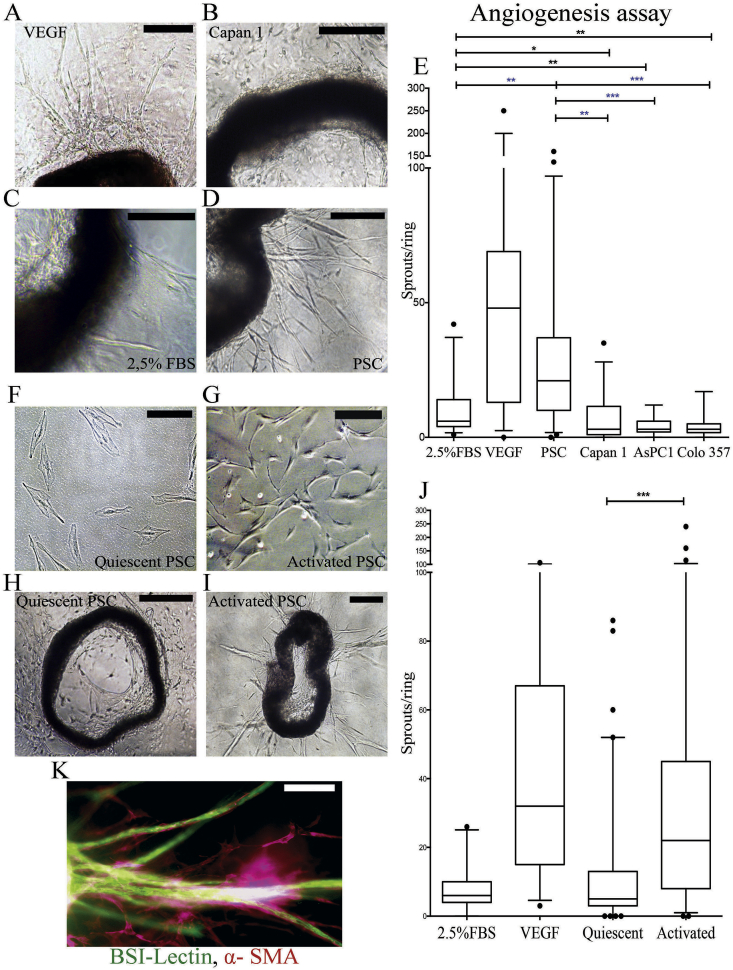
Fig. 4.
Stellate cells promote angiogenesis in mice aortic rings whereas cancer cells inhibit it. A–D: Representative microscopic images of aortic rings treated with either VEGF (30 ng/mL, positive control, A) [16], or conditioned medium from cancer cells (B), or negative controls (2.5% FBS supplemented media, C), or stellate cells (D) to demonstrate vessel sprouts at endpoint analysis. Scale Bar = 500 μm. E: The summary data of the aortic ring angiogenesis assays are shown in the form of box (median and interquartile ranges) and whisker (95% range) graphs. Each data-point represents an aortic ring with experiments performed in multiple replicates [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12] with at least three biological replicates. Statistical analyses were performed by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc multiple comparison. *p < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. F, G: ATRA treated pancreatic stellate cells show a quiescent morphology, whilst ethanol treated pancreatic stellate cells show the characteristic myofibroblast-like morphology. Scale Bar = 50 μm. H,I: Representative microscopic images of aortic rings treated conditioned medium from ATRA-treated PSC (H) or activated PSC (I) at endpoint analysis. Scale Bar = 500 μm (H) and 200 μm (I). J: The summary data of the aortic ring angiogenesis assays are shown in the form of box (median and interquartile ranges) and whisker (95% range) graphs. Each data-point represents an aortic ring with experiments performed in multiple replicates [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12] with at least three biological replicates. Statistical analyses were performed by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc multiple comparison. ***p < 0.001. K: Confocal microscope image of a sprout confirming the vascular nature of the sprouts. Vascular structures are stained with BSI-Lectin and supporting fibroblasts (pericytes) with smooth muscle actin (SMA). Scale bar: 100 μm. See Supplementary Fig. 2 for other analysis on effect of Collagen concentration.