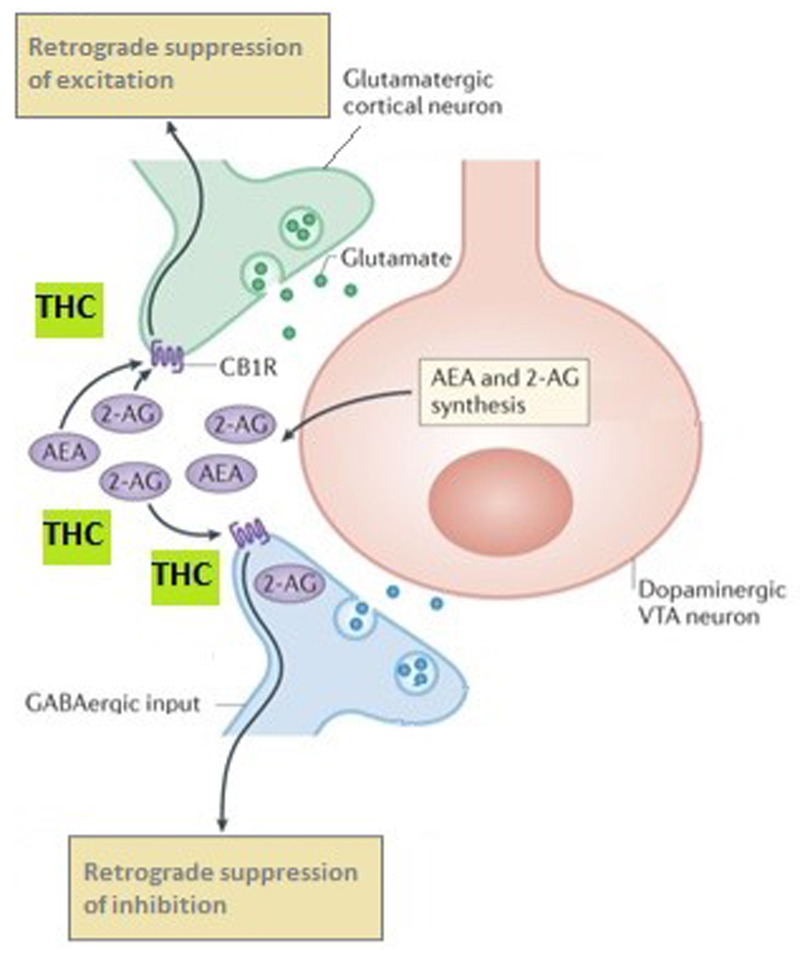
Fig. 1. THC binds to CB1 receptors on glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons disrupting normal endocannabinoid retrograde signalling from dopaminergic neurons137.
Endocannabinoids (eCBs) influence ventral tegmental area (VTA) synaptic signalling. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is synthesised by diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) in dopaminergic VTA neurons and, once released, retroactively acts on endocannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1Rs) on nearby glutamatergic and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic terminals. CB1Rs mediate robust inhibition of GABA inputs onto VTA dopamine cells29, termed retrograde suppression of inhibition. CB1Rs are also localized on glutamatergic terminals synapsing on VTA dopamine neurons30 where eCBs mediate retrograde suppression of excitation. Thus, eCBs fine-tune the activity of the mesolimbic dopamine projections through modulating both excitatory and inhibitory signalling. THC disrupts this finely tuned system.