Figure 6. Schematic representation of the proposed involvement of endocytic pathways in the regulation of ABCA1 endocytosis.
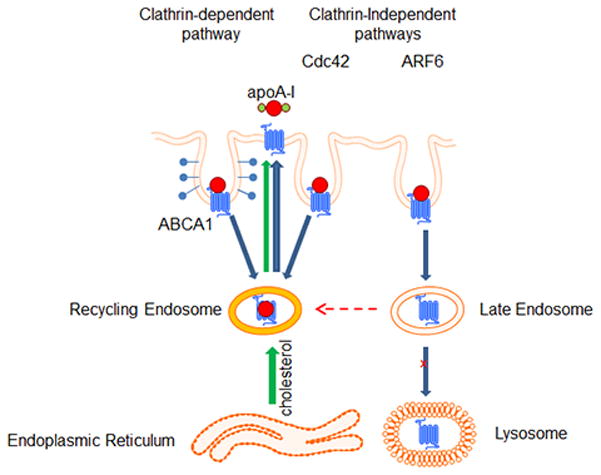
ARF6-dependent pathway is responsible for endocytosis of ABCA1 directing it into late endosomes followed by degradation of ABCA1. This pathway is responsible for regulation of the abundance of ABCA1 on cell surface. Other clathrin-dependent and clathrin-indepedndent pathways may be responsible for the recycling of ABCA1; they are not involved in regulation of ABCA1 abundance, but may be involved in the efflux of intracellular cholesterol. Endocytic pathways compete with each other and inhibition of ARF6 (degradation) pathway may re-direct ABCA1 into recycling pathways leading to increased activity of intracellular cholesterol efflux.
