Figure 1.
The m6A Machinery Regulates Infectious HCV Particle Production
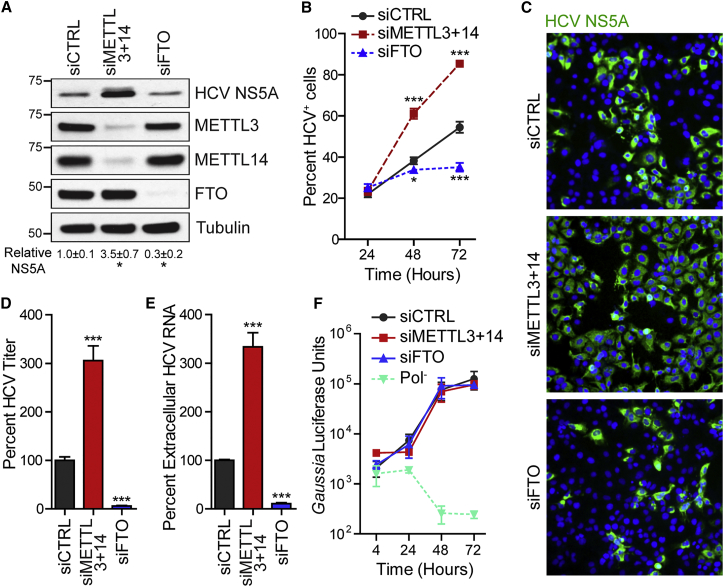
(A) Immunoblot analysis of extracts of HCV-infected Huh7 cells (72 hpi) treated with siRNAs. NS5A levels were quantified relative to tubulin (n = 3). ∗p ≤ 0.05 by unpaired Student’s t test.
(B) Percentage of HCV+ cells by immunostaining of NS5A and nuclei (DAPI) after siRNA. n = 3, with ≥5,000 cells counted per condition. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction.
(C) Representative fields of HCV-infected cells (NS5A+, green) and nuclei (DAPI, blue) at 72 hpi from (B).
(D and E) FFA of supernatants harvested from Huh7 cells 72 hpi after siRNA treatment (D). HCV RNA in supernatants harvested from Huh7 cells 72 hpi after siRNA treatment as quantified by qRT-PCR (E). Data are presented as the percentage of viral titer or RNA relative to control siRNA. ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001 by unpaired Student’s t test. Values are the mean ± SEM of three experiments in triplicate.
(F) Gaussia luciferase assay to measure HCV luciferase reporter (JFH1-QL/GLuc2A) transfected in Huh7.5 CD81 KO cells after siRNA treatment. Pol−, lethal mutation in HCV NS5B polymerase.
Values in (B) and (F) represent the mean ± SD (n = 3) and are representative of three independent experiments. See also Figure S1.