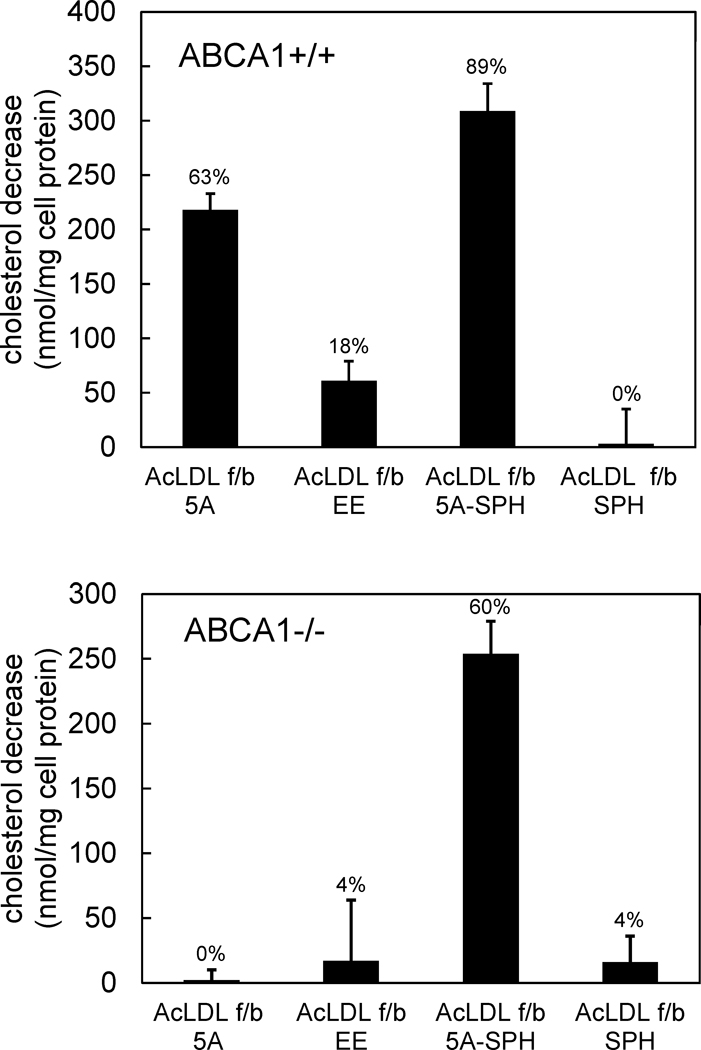
Figure 6. ApoA-I mimetic peptide 5A substantially decreases ABCA+/+ but not ABCA−/− mouse macrophage cholesterol content.
One-week-old mouse M-CSF differentiated bone marrow-derived macrophage cultures were incubated 2 days with 50 μg/ml AcLDL + 5 μm TO9 to enrich macrophages with cholesterol. Following rinsing, macrophage cultures were incubated 2 days with the indicated additions (100 μg/ml peptide and 125 μg/ml sphingomyelin alone or complexed with 100 μg/ml peptide 5A) without AcLDL. Then, the macrophage total cholesterol content was determined, and the decrease in macrophage cholesterol content induced by the added peptide was calculated. Cholesterol contents before and after incubation with AcLDL, respectively, were 107 ± 14 nmoles cholesterol/mg cell protein (10 ± 2% cholesteryl ester) and 453 ± 27 nmoles cholesterol/mg cell protein (70 ± 0% cholesteryl ester) for ABCA1+/+ macrophages, and 146 ± 26 nmoles cholesterol/mg cell protein (25 ± 10% cholesteryl ester) and 571 ± 7 nmoles cholesterol/mg cell protein (75 ± 1% cholesteryl ester) for ABCA1−/− macrophages. For ABCA1+/+ macrophages, 5A and 5A-SPH were significantly different than EE and SPH. For ABCA1−/− macrophages, 5A-SPH was significantly different than 5A, SPH, and EE. AcLDL, acetylated low-density lipoprotein; TO9, TO901317; f/b, followed by; 5A, peptide 5A; EE, peptide EE; 5A-SPH, peptide 5A-sphingomyelin complex; SPH, sphingomyelin.