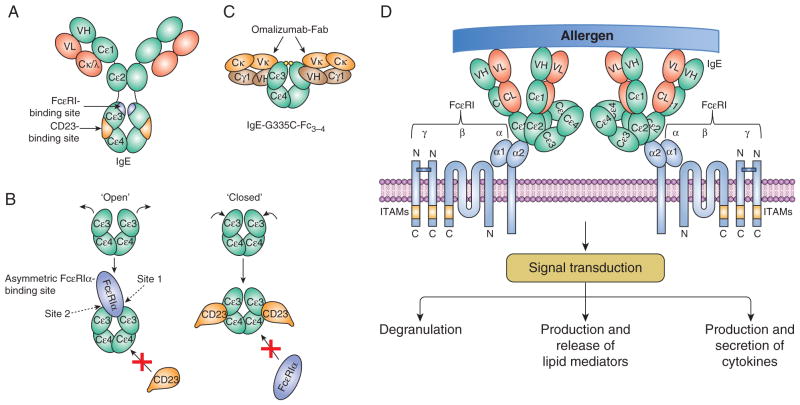
Figure 2. IgE, its interaction with omalizumab, and FcεRI-mediated mast cell activation.
(A) IgE and the relative locations of the FcεRIα- and CD23-binding sites. (B) Open and closed conformations of the IgE-Fcε3–4 domains interacting with FcεRIα and CD23, respectively. (C) Symmetric interaction of two omalizumab Fabs with IgE-Fcε3–4. Modified from Pennington et al. (63). (D) Crosslinking of IgE-bound FcεRI with a multivalent allergen leads to activation of mast cells. The activated cells degranulate and produce/release lipid mediators and cytokines. Signal transduction via the FcεRI was recently reviewed (124–127). Domains of IgE and omalizumab are represented by ovals. ITAMs, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs.