| Box 1: Functions of selected chemosensory neurons involved in C. elegans microcircuits | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuron: |

|

|

|

|

|
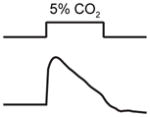
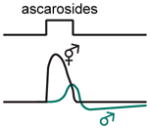
| Senses: | odors, temperature, CO2, salt, osmotic stress, pH | odors | odors, soluble chemicals, mechanical and osmotic stimuli | CO2, O2 | odors, pheromones |
Schematic of activity: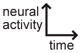
|
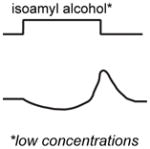
|
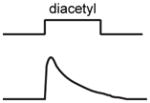
|
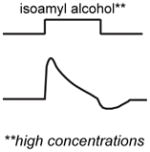
|
|
|
| Valence promoted: | attraction | attraction | avoidance |
avoidance
(adults) attraction (dauers) |
avoidance |
| Relevant interactions: |
|
|
|
|
|

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.