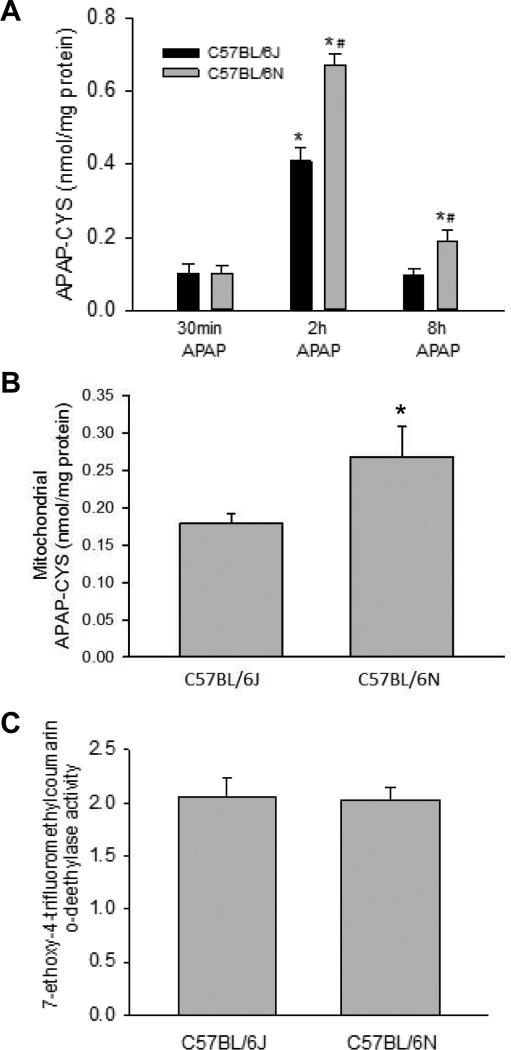
Figure 3.
APAP-protein adduct formation and P450 activities in C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mice. C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mice were treated with 200 mg/kg APAP or saline as control. APAP-cysteine adducts were quantified by HPLC-ED in liver homogenate at 30 min, 2h and 8h post-APAP (A) or mitochondria (B) at 2 h post-APAP (peak of adduct formation) in C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mice. Cytochrome P450 activities were measured in the 14,000×g supernatant of control mouse liver homogenate using the 7EFC deethylase assay (C). Data represent means ± SE of n=4 animals per group. *p< 0.05 (compared with C57BL/6J mice, t=0).